Second Monitor Not Detected: This comprehensive guide dives into the various reasons why your second monitor might not be showing up. From potential hardware issues to complex operating system configurations, we’ll explore a range of troubleshooting scenarios to help you get your dual-monitor setup back up and running.
We’ll cover everything from checking cable connections and driver updates to adjusting display settings and diagnosing potential hardware conflicts. This guide is your one-stop resource for tackling the “second monitor not detected” problem, no matter the cause.
Troubleshooting Scenarios
A second monitor not being detected can be a frustrating issue, but often a simple fix resolves the problem. This section explores various scenarios and troubleshooting steps to help you diagnose and resolve this common display problem.
Potential Hardware Issues
Several hardware-related problems can prevent a second monitor from being recognized. Faulty cables, defective video cards, or even issues with the monitor itself are possibilities. Physical damage to any of these components can also contribute to the problem.
- Faulty video card: A malfunctioning graphics processing unit (GPU) can prevent the system from recognizing a connected monitor. Symptoms might include the monitor displaying garbled images or not displaying at all.
- Defective monitor: A failing monitor might not respond to signals from the computer, resulting in the “not detected” issue. Check the monitor’s power supply and input signals.
- Damaged cables: Loose connections, bent pins, or physical damage to the cables (HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA) can prevent the signal from reaching the monitor. Always check for any signs of damage to the cable before attempting other solutions.
- Incorrect connection type: Using the wrong type of connection (e.g., connecting an HDMI cable to a DisplayPort port) will not allow the monitor to receive the signal and will cause detection failure.
Software Conflicts
Software-related issues can also cause the problem. Drivers, operating system settings, or even conflicting applications might interfere with the monitor detection process.
- Outdated or corrupted drivers: Graphics card drivers are essential for proper communication between the computer and the monitor. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause problems with signal recognition.
- Conflicting applications: Certain applications might interfere with the operating system’s ability to detect and configure the second monitor. If a new application was installed recently, try uninstalling it and checking if the monitor is detected.
- Operating system issues: Sometimes, a problem within the operating system itself can lead to the second monitor not being recognized. This can manifest as a general system instability issue, or specific display issues.
Operating System Variations
Different operating systems (Windows and macOS) have varying approaches to handling multiple monitors. Understanding these differences is important for effective troubleshooting.
- Windows 10/11: Windows utilizes display settings to manage multiple monitors. Problems might stem from incorrect display resolution settings, display mode conflicts, or issues with the display adapter.
- macOS: macOS uses similar principles to manage multiple monitors, with display settings and configurations playing a crucial role. Issues can be caused by conflicts with screen resolution or incorrect display settings.
Post-Update/Driver Installation Issues
After a system update or driver installation, the second monitor might stop working due to compatibility issues or configuration changes.
- Compatibility issues: A recent update might not be compatible with the second monitor’s driver or hardware. This could result in the system not recognizing the second display.
- Incorrect configuration: The update might alter display settings, causing the second monitor to be misconfigured. This could involve incorrect resolutions, refresh rates, or display modes.
Troubleshooting Steps Based on Connection Type
Troubleshooting steps vary based on the type of connection used for the second monitor.
- HDMI: Verify the HDMI cable’s integrity and ensure a secure connection to both the monitor and the computer. Check the monitor’s input settings to ensure the correct HDMI input is selected.
- DisplayPort: Similar to HDMI, check the DisplayPort cable’s integrity and secure connections. Confirm the monitor’s input selection matches the DisplayPort port.
- VGA: Ensure the VGA cable is properly connected and that the correct VGA input is selected on both the monitor and the computer. Ensure the monitor is receiving power.
Cable Connections and Security, Second Monitor Not Detected
Proper cable connections are critical for signal transmission. Loose or improperly seated cables can lead to signal interruptions, causing the second monitor not to be detected.
- Secure connections: Ensure all cables are firmly plugged into the appropriate ports on both the monitor and the computer. Loose connections can prevent the display signal from reaching the monitor.
Monitor Settings and Display Configurations
Incorrect monitor settings or display configurations can cause the system to fail to recognize the second monitor.
- Resolution settings: Ensure the resolution settings for the second monitor are compatible with the system. Incompatible resolutions can lead to detection failures.
- Display mode: Verify that the display mode for the second monitor is set correctly. This includes ensuring the monitor is set to the correct input source.
Display Port Compatibility
| Display Port Type | Compatibility with Devices |
|---|---|
| HDMI | Most modern computers and monitors |
| DisplayPort | High-end monitors and computers |
| VGA | Older computers and monitors |
Driver-Related Issues
Driver conflicts are a frequent culprit behind second monitor problems. Outdated or incompatible graphics card drivers can prevent your system from recognizing the additional display. This section details how to identify, update, and resolve driver-related issues that might be preventing your second monitor from displaying.Often, the solution involves updating or reinstalling the graphics card drivers. Incorrect or outdated drivers can cause a multitude of issues, from poor performance to complete failure of certain components.
Having trouble with your second monitor not being detected? Sometimes, fiddling with display settings isn’t enough. If you’re also looking to create a truly unique VRchat avatar, you might find some helpful troubleshooting tips for your display settings by checking out how to Make a Vrchat Avatar. It’s often a good idea to verify your graphics card drivers and monitor connections are all up to date before you dive into more advanced solutions for a second monitor not detected issue.
This section provides the necessary steps to resolve these conflicts, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
Identifying Potential Driver Conflicts
Driver conflicts can manifest in various ways, including the second monitor not being recognized at all, displaying intermittently, or showing a distorted image. Sometimes, the problem is subtle, with the second monitor appearing but having limited functionality, such as a lack of refresh rate options. It’s essential to meticulously check for these symptoms to pinpoint the root cause.
Driver conflicts can also arise due to a mismatch between the graphics card driver and the operating system version, or the monitor’s driver. A critical step is to confirm the driver version and its compatibility with your hardware and operating system.
Updating or Reinstalling Graphics Card Drivers
Updating drivers is crucial for maintaining compatibility and functionality. Using outdated drivers can lead to stability problems, performance issues, and the failure to detect peripherals. The process involves downloading the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website, usually the graphics card’s manufacturer.
Uninstalling and Reinstalling Display Adapters
Sometimes, reinstalling display adapters can resolve problems stemming from corrupted or outdated driver files. This process removes existing drivers and allows the system to reinstall them correctly. This approach can help resolve compatibility issues, fix glitches, and improve overall performance. It’s important to note that uninstalling and reinstalling drivers should only be attempted as a last resort if other troubleshooting steps fail.
Verifying Graphics Card Driver Version and Compatibility
Ensuring compatibility between the graphics card driver, operating system, and monitors is critical. A mismatched driver can cause problems with the second monitor’s resolution, refresh rate, or overall display. Incorrect versions can also hinder or entirely prevent the recognition of the second display. Checking the driver version is often available within the device manager. Verify the driver’s compatibility with your operating system (e.g., Windows 10, Windows 11) and monitor specifications.
My second monitor just isn’t showing up, which is a real bummer. I was hoping to finally get some serious work done, but now I’m stuck trying to figure out why it’s not connecting. Maybe I should check out some upbeat tunes to help me troubleshoot, like Corin Tucker’s bands stream corin tucker bands kill my blues in full.
Hopefully, a little music will inspire me to find the solution to this second monitor issue! Fingers crossed it’s a quick fix.
Compatibility information is usually available on the manufacturer’s website.
Using the Correct Monitor Drivers
Using the correct monitor drivers is essential for optimal display performance. Incorrect or outdated monitor drivers can result in various issues, including reduced display quality, color inaccuracies, and issues with screen resolution. Using the manufacturer’s official drivers, downloaded directly from their website, is crucial for ensuring proper functionality and compatibility. If the monitor manufacturer’s website doesn’t have updated drivers, check the manufacturer’s support forums or community pages.
Common Graphics Card Driver Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Driver conflict with other hardware | Uninstall conflicting drivers or update them. Check for compatibility issues between the drivers. |
| Outdated drivers | Download and install the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website. |
| Corrupted drivers | Uninstall and reinstall the display adapters. |
| Driver incompatibility with operating system | Ensure the driver version is compatible with the operating system. |
| Driver incompatibility with monitor | Ensure the monitor’s driver is compatible with the graphics card driver. If possible, update the monitor driver as well. |
Operating System Configurations: Second Monitor Not Detected
Your operating system plays a crucial role in recognizing and managing multiple monitors. Proper configuration ensures seamless display of content across both screens. Incorrect settings can lead to the second monitor not being detected, resulting in a frustrating experience. Understanding how to configure your OS display settings is essential for troubleshooting this issue.
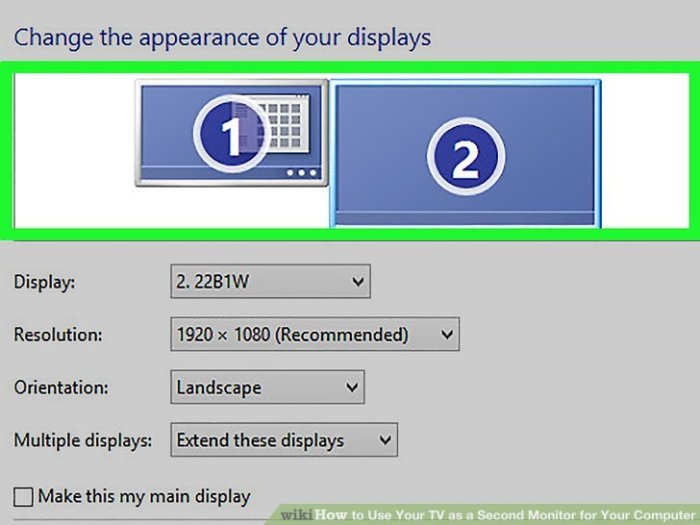
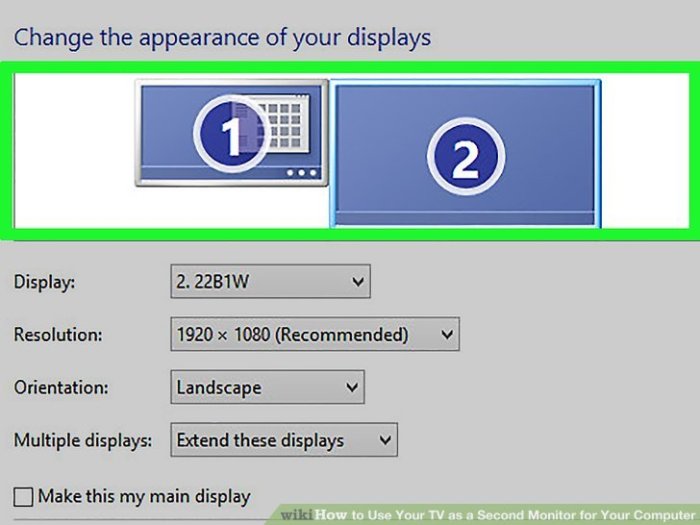
Display Settings Adjustments
Adjusting display settings is a critical step in ensuring your second monitor is properly recognized. This involves configuring the resolution, refresh rate, and display mode for both screens. These settings determine how your operating system interacts with each monitor, impacting the detection process.
- Resolution Selection: Selecting the correct resolution for each monitor is paramount. Using incompatible resolutions can cause issues with detection. The resolution should match the physical capabilities of the monitor. For example, if one monitor supports 1920×1080, and the other 1920×1200, you need to adjust the settings accordingly. Using a resolution that is too high for the monitor’s capabilities will lead to visual artifacts or a complete failure to display on the monitor.
- Refresh Rate Adjustment: The refresh rate dictates how many times per second the image on the screen is updated. Mismatched refresh rates between monitors can also lead to issues with the display and detection. Matching or selecting compatible refresh rates for both monitors is essential for a seamless experience. A common cause of display issues is trying to use a refresh rate that the monitor does not support.
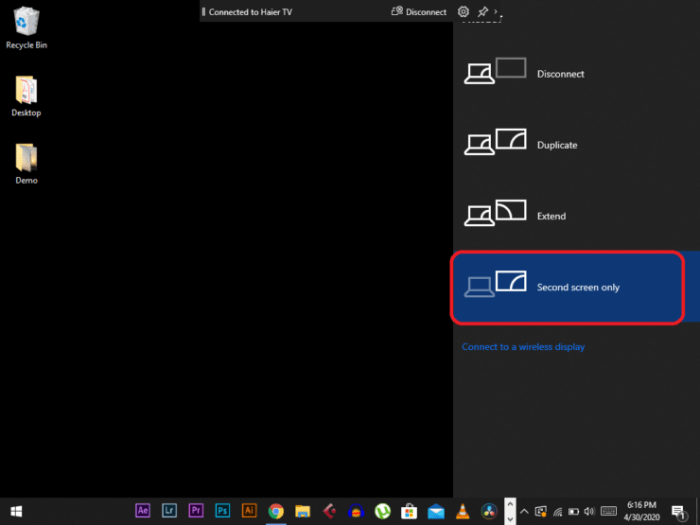
- Display Mode Selection: The display mode dictates how the operating system arranges the screens. Common modes include “Extend these displays,” “Duplicate these displays,” and “Single display.” “Extend these displays” is often the preferred mode for utilizing both screens as separate workspaces. Incorrect display modes can result in only one screen being detected. Always choose the mode that suits your workflow.
Display Settings Files
Corrupted display settings files can sometimes lead to issues in recognizing the second monitor. These files store crucial information about the display configuration, and corruption can lead to errors.
- System File Integrity: System file integrity checks can help identify and repair corrupted display settings files. This ensures the operating system’s files are consistent and working correctly. This is a critical step to resolve unexpected issues.
- Resetting Display Settings: A simple reset of display settings to their default values can resolve various issues related to corrupted settings. This often involves using the operating system’s built-in tools to revert the settings to their initial state. Ensure you save your current settings before making this change.
Resolution and Refresh Rate Comparison
Choosing appropriate resolution and refresh rates is crucial for optimal display performance and monitor detection. Mismatched settings can lead to blurry images or a failure to detect the second monitor.
| Resolution | Refresh Rate (Hz) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1920×1080 | 60 | Standard HD resolution, suitable for general use. |
| 2560×1440 | 144 | Wide-screen resolution, offering a sharper image, suitable for demanding tasks. |
| 3840×2160 | 120 | Ultra HD resolution, providing a highly detailed image, suitable for professional work. |
Monitor-Specific Problems
Sometimes, the culprit behind a second monitor not being detected isn’t your computer, but the monitor itself. A faulty monitor can prevent it from being recognized by your system, regardless of your computer’s configuration. Understanding monitor-specific issues is crucial for accurate troubleshooting.
Monitor Power and Functionality
Proper power is fundamental to monitor operation. Ensure the monitor is plugged into a functional power outlet and that the power switch (if present) is turned on. Look for visual indicators like the power LED, which should illuminate when the monitor is receiving power. If the LED remains off or blinks erratically, the monitor might have a power supply issue.
A functioning monitor will display a clear image and respond to input signals. If the image is distorted, blurry, or absent, the monitor itself might be faulty.
Compatibility and Graphics Card
Compatibility issues between the monitor and your computer’s graphics card can also cause detection problems. Different monitors support different resolutions, refresh rates, and input signals (e.g., DisplayPort, HDMI). Ensure your monitor’s specifications are compatible with your graphics card’s capabilities. For example, a monitor designed for a lower resolution might not work properly with a high-end graphics card capable of displaying a much higher resolution.
Check your graphics card’s specifications to confirm compatibility with your monitor’s specifications.
Monitor Settings and Configurations
Monitor settings can sometimes interfere with detection. Incorrect display settings on the monitor, like incorrect resolution or refresh rate, can prevent the monitor from being recognized by the computer. The monitor’s settings should match the graphics card’s capabilities and the operating system’s display settings. Verify that the monitor is set to the correct input signal (e.g., DisplayPort, HDMI).
Adjusting the monitor’s settings to match your computer’s capabilities is essential.
My second monitor just isn’t showing up, which is a real bummer. I was really looking forward to watching Solange’s incredible performance of “Cranes in the Sky” and “Don’t Touch My Hair” on SNL, which you absolutely have to check out. Hopefully, a quick fix will get me back to enjoying my music videos and other visual entertainment without a hitch.
This monitor issue is seriously getting in the way of my productivity!
Cable Connections and Ports
Incorrect or damaged connections can prevent your computer from recognizing the monitor. Ensure the cables connecting the monitor to the computer are properly seated in the appropriate ports. Loose or damaged cables, or faulty ports on either the monitor or the computer, can lead to detection issues. Inspect the cables for any visible damage, and if possible, try using a different cable to confirm if the problem lies with the cable itself.
Manufacturer Support and Recommended Settings
Consult your monitor’s manufacturer for support and recommended settings. The manufacturer’s website typically provides troubleshooting guides, FAQs, and specific instructions for setting up and using their monitors. Check for updates to the monitor’s drivers or firmware to ensure optimal compatibility. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for optimal performance and compatibility.
Monitor Brand-Specific Issues
| Monitor Brand | Potential Issues |
|---|---|
| Acer | Known for occasional driver compatibility problems, particularly with older models. |
| LG | Some users report issues with certain models and specific operating systems, especially if the monitor’s display settings are not properly configured. |
| Samsung | Display signal issues can arise if the monitor is not properly calibrated to the input signal from the graphics card. |
| BenQ | Some users report difficulties in recognizing the monitor on certain systems, often due to incorrect display port configurations or conflicting drivers. |
| HP | Potential for display signal interference when using older models, especially when connected through older versions of the display port. |
This table provides a general overview of potential issues, but individual experiences may vary.
Hardware Conflicts and Solutions

Troubleshooting second monitor issues often involves delving into potential hardware conflicts. These conflicts can arise from various sources, from incompatible components to subtle malfunctions. Understanding these conflicts and their potential resolutions is crucial to restoring a stable multi-monitor setup.
Potential Conflicts Between Graphics Card and Other Hardware
Hardware components can sometimes interfere with each other, especially when sharing resources like PCI Express lanes or system memory. A conflicting device might consume resources necessary for the graphics card to properly communicate with the second monitor. This can manifest as the second monitor not being detected or displaying improperly.
Diagnosing and Resolving Hardware Conflicts
To pinpoint the source of a hardware conflict, a systematic approach is essential. Begin by examining the hardware components connected to the computer. Ensure all connections are secure and free of any physical damage. Unplug any recently added peripherals or devices, one by one, to isolate the problem.
Checking for Conflicting Devices or Software
System resource conflicts can also stem from software interference. Check the device manager to identify any unrecognized or malfunctioning hardware devices. Update or reinstall drivers for suspect components, particularly the graphics card and the monitor. Review any recently installed software or drivers that might be competing for system resources. A utility program for monitoring system resources can assist in detecting such issues.
Importance of Checking for Hardware Malfunctions
Hardware malfunctions, including failing components like the graphics card or RAM, can lead to various issues, including the inability to detect a second monitor. Check for physical damage or overheating symptoms on all hardware components. A faulty component may not be immediately apparent, yet its subtle failures can cascade into larger problems like the inability to display the second monitor.
Replacing malfunctioning components is crucial to ensuring reliable system performance.
Identifying Potential Overheating Issues
Overheating can severely impact the performance of hardware components, including the graphics card. Overheating can manifest as graphical glitches, slowdowns, or the second monitor going black. Regularly check the internal temperature of the computer using monitoring software or a hardware diagnostic tool. Ensure proper airflow around the computer to maintain a suitable operating temperature.
Table of Possible Hardware Conflicts and Solutions
| Potential Hardware Conflict | Possible Solution |
|---|---|
| Conflicting PCI Express lanes | Reinstall drivers for the graphics card. Check for conflicts with other PCI Express devices. |
| Faulty RAM | Run a RAM test using diagnostic tools. Replace faulty RAM modules. |
| Overheating graphics card | Ensure proper airflow in the computer case. Use a cooling pad for the graphics card if needed. |
| Failing power supply | Check the power supply for any damage. Replace if necessary. |
| Conflicting USB devices | Disconnect any recently added USB devices to isolate the conflict. |
Advanced Troubleshooting

Persistent second monitor issues often require a deeper dive than basic checks. This section details advanced troubleshooting techniques, leveraging system information tools, device manager, diagnostics, and system logs to pinpoint and resolve stubborn problems. A systematic approach is crucial for isolating the root cause.Advanced troubleshooting involves a methodical approach, progressing from general system checks to more specific diagnostics, enabling you to identify the source of the problem and implement the most effective solution.
Using System Information Tools
System information tools provide a comprehensive view of your hardware and software configuration. This information is vital for identifying potential conflicts or incompatibilities that might be hindering second monitor detection. Tools like System Information (msinfo32.exe) or the Windows System Information tool offer detailed reports on the installed hardware, drivers, and operating system, providing insights into potential problems.
Utilizing Device Manager
Device Manager is a valuable tool for inspecting and managing device drivers. Display adapter issues can manifest as detection problems. Inspecting the display adapter in Device Manager allows for the identification of problematic drivers. Right-clicking the display adapter and selecting “Properties” reveals detailed information about the driver, including its status and any reported errors. Identifying and updating outdated drivers or resolving conflicts can resolve display issues.
Examine the device’s properties for any warnings or error codes, which can offer clues about the underlying problem.
Running Graphics Card and Monitor Diagnostics
Dedicated diagnostics for graphics cards and monitors provide valuable insights into hardware health. Graphics card manufacturers often provide utility software for running hardware tests, helping identify potential problems with the graphics card itself. These tools may help identify issues such as memory errors or malfunctioning components. Monitor diagnostics are also available and should be performed if the monitor’s functionality is suspected to be at fault.
These tests can pinpoint defects in the monitor’s hardware, such as backlight issues or pixel problems. If the diagnostics reveal problems, consider replacing the faulty component.
Analyzing System Logs
System logs contain a record of events occurring on your system, including those related to the display. Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc) is a valuable resource for identifying errors or warnings related to the display adapter. Specific error codes or messages in the system logs can indicate the cause of the detection problem. Examining the logs for error messages related to the display can help pinpoint the root cause of the issue.
Troubleshooting Table
| Troubleshooting Step | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Verify driver compatibility | Ensures the driver for the graphics card and monitor are compatible with the operating system. |
| Check for hardware conflicts | Identifies any hardware conflicts that might be preventing the second monitor from being detected. |
| Run diagnostics on the graphics card and monitor | Evaluates the hardware health of the graphics card and monitor for potential issues. |
| Inspect system logs | Finds error messages or warnings related to the display, providing clues about the problem’s cause. |
| Update drivers | Ensures the most current drivers are installed, fixing compatibility problems or resolving errors. |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, resolving the “second monitor not detected” issue often involves a systematic approach. We’ve examined potential hardware problems, software conflicts, and operating system configurations. By thoroughly checking connections, updating drivers, and adjusting settings, you should be able to identify and fix the root cause of the problem. If the issue persists, consider reaching out to manufacturer support or seeking further technical assistance.