Lock Cells in Excel is a powerful technique for protecting your spreadsheet data. It allows you to prevent accidental changes, creating secure and user-friendly worksheets. This guide will walk you through various methods for locking cells, from basic protection to advanced password-locking and specific cell range controls. Learn how to safeguard your data and create professional-looking spreadsheets.
Whether you’re building financial reports, inventory trackers, or complex data models, locking cells can significantly improve data integrity. We’ll explore practical applications and troubleshoot potential problems, ensuring you master this essential Excel skill.
Introduction to Locking Cells in Excel
Locking cells in Excel is a powerful technique to protect specific data from accidental modification. It’s a crucial feature for maintaining data integrity and consistency within spreadsheets, especially in collaborative environments. This method allows you to designate certain cells as read-only, preventing users from unintentionally altering their contents.By strategically locking cells, you can safeguard formulas, important calculations, and critical data entry points, leading to more reliable and accurate spreadsheets.
This control over cell modification contributes to improved data quality and reduces the likelihood of errors.
Defining Locking Cells
Locking cells in Excel means preventing users from changing the values, formulas, or formatting of designated cells. These cells remain fixed and cannot be modified, providing a degree of protection.
Purpose and Benefits of Locking Cells
Locking cells is essential for maintaining data accuracy and consistency. By restricting modifications, you can safeguard critical data points, ensuring that only authorized individuals or groups can alter them. This is especially useful in shared spreadsheets where multiple users might be working on the same document.
Protecting a Worksheet vs. Locking Cells
Protecting a worksheet is a broader security measure that locks the entire worksheet, preventing any modifications. Locking cells, however, provides more granular control. You can choose which cells to lock and which to leave unlocked, offering a tailored level of protection. This allows for a greater degree of flexibility in controlling access to specific information within a worksheet.
Common Scenarios for Locking Cells
Locking cells is highly useful in various situations. For example, in financial reports, locking cells containing pre-defined formulas prevents accidental changes that could compromise the accuracy of the calculations. Similarly, in data entry forms, locking cells used for summary calculations protects the data integrity of the final report. Moreover, in shared spreadsheets, locking cells containing constants or look-up values ensures that everyone uses the same, correct data.
Basic Example of Locked and Unlocked Cells
This table illustrates the concept of locked and unlocked cells. The table displays data that is protected by locking certain cells, while others remain modifiable. This demonstrates the granular control afforded by locking cells within a spreadsheet.
| Column A (Locked) | Column B (Unlocked) |
|---|---|
| 2023 Sales Target | Sales Rep |
| $1,000,000 | John Smith |
| $1,200,000 | Jane Doe |
| $1,500,000 | David Lee |
In this example, Column A (containing sales targets) is locked, preventing users from changing these values. Column B (containing sales representatives) is unlocked, allowing users to update this information. This separation of modifiable and non-modifiable data provides a clear visual distinction for data protection.
Methods for Locking Cells
Securing specific cells in your Excel spreadsheets is crucial for maintaining data integrity and preventing accidental modifications. This article details various methods for locking cells, enabling you to protect sensitive information and enforce data consistency. Understanding these techniques empowers you to create more robust and reliable spreadsheets.
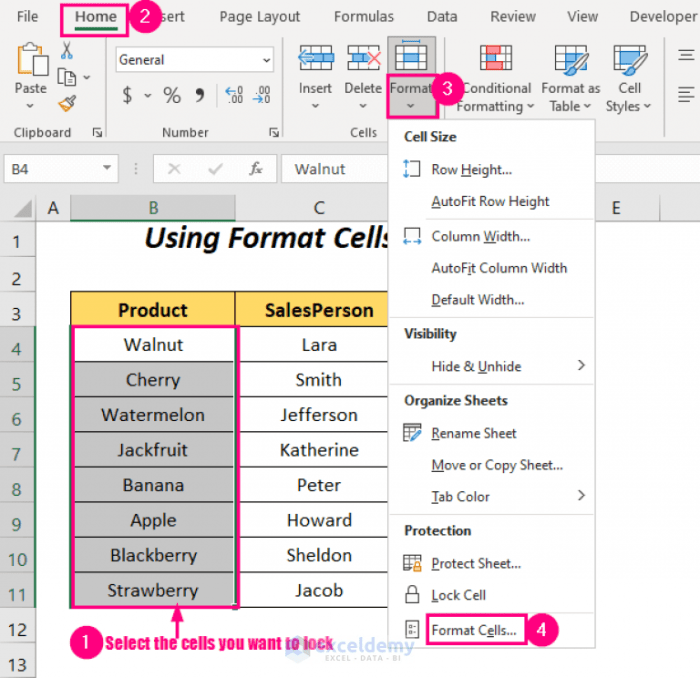
Using the Format Cells Option
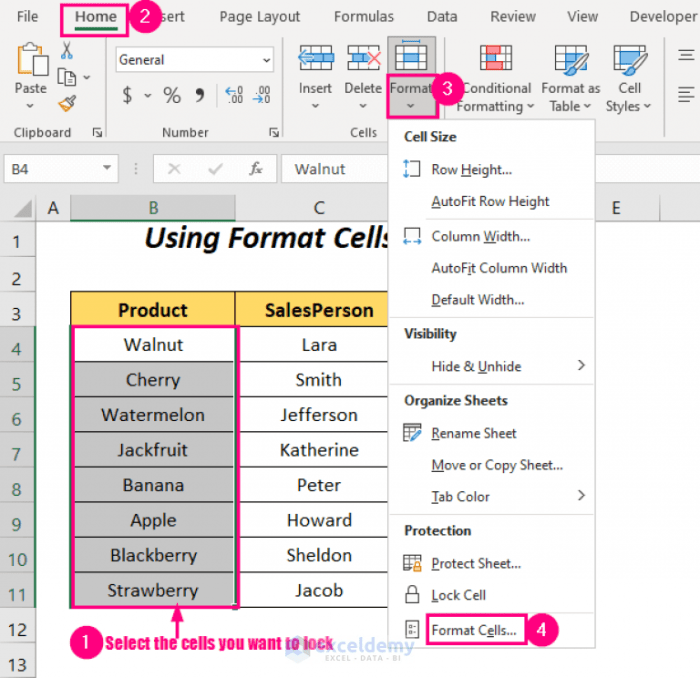
This method allows you to lock individual cells directly. Select the cells you want to protect. Right-click and choose “Format Cells.” Navigate to the “Protection” tab. Check the “Locked” box. This locks the cells, preventing any changes to their values.
Crucially, remember that locking a cell does not automatically protect it; a sheet protection step is still required.
Protecting the Sheet
Protecting a sheet is a fundamental step to enforce the locking of cells. After locking cells using the Format Cells option, you must protect the sheet. Select “Review” on the Excel ribbon. Click “Protect Sheet.” Enter a password (optional but highly recommended) to safeguard the protection. Specify which cells or ranges should be locked by selecting “Locked cells.” This prevents users from changing protected cells, even if they are allowed to edit the rest of the sheet.
Locking Cells with VBA
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) offers a powerful and flexible way to lock cells programmatically. This method is ideal for complex scenarios or automated tasks. VBA code allows you to specify the cells to lock dynamically, making it well-suited for large datasets or recurring tasks. You can use VBA to lock specific cells in a sheet, or to control the locking of cells based on certain conditions or events.“`VBASub LockCells() Dim rng As Range Set rng = Range(“A1:B5”) ‘Specify the range to lock With rng .Locked = True .Interior.Color = vbYellow End With ActiveSheet.Protect DrawingObjects:=False, Contents:=True, Scenarios:=False, Password:=”mypassword”End Sub“`This example locks cells A1 through B5 and highlights them in yellow.
The password is crucial to protect the locked cells from unauthorized access.
Comparison of Methods
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Format Cells | Locks cells individually | Simple for single cell locking | Not suitable for complex locking schemes. |
| Protect Sheet | Enforces locking of cells after locking with Format Cells | Easy to implement, good for basic protection | Can be cumbersome for advanced protection. |
| VBA | Dynamic locking via code | Highly flexible, suitable for complex logic | Requires VBA knowledge |
This table summarizes the key characteristics of each method, aiding in the selection of the most appropriate technique for your specific needs. Choosing the right method depends on the complexity of your spreadsheet and the level of protection you require.
Advanced Locking Techniques: Lock Cells In Excel
Mastering cell locking in Excel goes beyond basic protection. Advanced techniques allow for more granular control, ensuring data integrity and preventing unintended modifications. This involves password protection, targeted cell range locking, and handling formulas and charts within the locked structure. These methods provide a more robust security layer for your spreadsheets.
Password Protection for Locked Cells
Password protection adds an extra layer of security to locked cells. This prevents unauthorized access even if the worksheet is unlocked. It is crucial for sensitive data. Enter the password when setting the protection and again whenever you need to modify the protected cells.
Locking Specific Cell Ranges
Locking specific cell ranges allows for greater control over protected areas. Instead of locking the entire worksheet, you can select and protect only the cells containing crucial data, maintaining flexibility for other, non-sensitive areas. This ensures that only designated cells are restricted.
Locking Cells Containing Formulas
Formulas, crucial parts of spreadsheets, can be locked to prevent unintended changes to their logic. Locking these cells maintains the integrity of calculations. This is especially important for complex models and financial projections where formula alterations could lead to inaccurate results.
Learning to lock cells in Excel is super helpful for creating spreadsheets that stay organized. It’s a fundamental skill, like knowing how to design your dream Sims home in The Sims 4. Make Sims Inspired in The Sims 4 is a great resource if you want to design some cool characters! Once you master locking cells, you can prevent accidental changes, making your spreadsheets much more reliable.
This is crucial for maintaining accurate data.
Locking Cells That Are Part of a Chart
Locking cells that are part of a chart is essential for maintaining data consistency. Protecting the data source cells ensures that any changes reflected in the chart accurately represent the underlying data. This is important when updating the source data without affecting the chart’s integrity.
Example: Password Protection and Cell Range Locking
The following example demonstrates password protection and cell range locking in a practical scenario. It uses a simple HTML table to represent the spreadsheet.
| Product | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Product A | ||
| Product B |
The price and quantity cells are locked. These values cannot be directly modified by users. This ensures that the underlying data used for the chart remains consistent and unchanged.
To lock the cells in the table, select the cells, right-click, and choose “Format Cells”. Then select the “Protection” tab and check the “Locked” box. To apply password protection, go to “Review” > “Protect Sheet”.
Important Note: This example uses HTML table representation. Actual Excel implementation will involve the Excel application’s tools and functions for cell locking and password protection.
Practical Applications of Locked Cells
Locking cells in Excel offers significant advantages beyond basic protection. It empowers users to create robust spreadsheets that prevent accidental modifications, ensuring data integrity and consistency. This is crucial for collaborative projects, user-friendly forms, and protected templates, ultimately enhancing the overall security of the spreadsheet.By understanding how to lock cells, you can design spreadsheets that are not only functional but also resilient to errors and misuse.
This control extends beyond simple protection, enabling more complex functionalities like user-specific data entry and customized reporting.
Locking cells in Excel is crucial for protecting data, especially when collaborating. It’s like creating a safe zone for specific parts of your spreadsheet. Just like how Kendrick Lamar’s DNA gets a new version for the NBA finals, this new twist on the NBA Finals theme requires some carefully considered adjustments. Knowing which cells to lock ensures your data stays secure and avoids accidental edits, keeping your spreadsheets organized and your work efficient.
Preventing Accidental Data Modification
Accidental changes to critical data can lead to errors and wasted time. Locked cells provide a crucial safeguard against this. Imagine a spreadsheet tracking financial data; if certain cells containing formulas or predefined values are locked, users cannot inadvertently alter these critical elements, thus maintaining the integrity of the calculations. This feature is vital for preventing errors and maintaining data accuracy in collaborative environments.
Creating User-Friendly Forms
Locked cells are essential for designing user-friendly forms in Excel. A form for collecting customer information, for example, could lock cells that automatically calculate totals or contain pre-defined formulas. Users can then input data into specific fields without inadvertently altering the calculations or format of the form. This approach makes the form straightforward and intuitive to use, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
Creating Protected Templates
Locked cells are vital for creating protected templates. Consider a template for invoices. Locking the cells containing headers, formulas for calculating amounts, or predetermined formatting ensures that users cannot change the structure or calculations of the template. This ensures that all invoices adhere to the required format and calculations, maintaining consistency and accuracy.
Enhancing Data Security
Locking cells is a fundamental step in data security. By locking cells containing sensitive information, you restrict access to those values. For example, a spreadsheet with confidential financial data could lock all cells containing sensitive financial figures. This method significantly strengthens the security of the spreadsheet, preventing unauthorized modifications and ensuring the confidentiality of the data.
Locking cells in Excel is a pretty handy feature, especially when you’re working with spreadsheets that need to be protected from accidental edits. It’s all about safeguarding data integrity. This reminds me of the recent initiative in the grand duchy, where the people are being given a voice, grand duchy let the people speak , a great example of how letting the public share their opinions can lead to better outcomes.
Ultimately, locking cells is about maintaining order and accuracy within the spreadsheet.
Visual Demonstration, Lock Cells in Excel
| Application | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Preventing Accidental Modification | Locking cells containing formulas or constant values to maintain data integrity. | A spreadsheet calculating employee salaries. The salary structure (basic pay, allowances) is locked, preventing users from altering these values. |
| Creating User-Friendly Forms | Locking cells containing formulas or pre-defined formatting to prevent unintended modifications. | A customer survey form with locked calculation fields. Users input data, and the form automatically calculates totals. |
| Creating Protected Templates | Locking cells containing headers, calculations, or formatting to maintain template consistency. | An invoice template with locked headers, calculation fields, and currency formatting. |
| Enhancing Data Security | Locking cells containing sensitive information to restrict unauthorized modifications. | A spreadsheet with confidential financial data. Cells containing account balances, transaction details, or sensitive information are locked. |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Locking cells in Excel can be a powerful tool, but it’s essential to understand how to address potential problems. Incorrect configurations or user errors can lead to unexpected results. This section details common issues encountered when working with locked cells, along with their solutions and preventative measures.Troubleshooting locked cells involves identifying the root cause of the problem and applying appropriate fixes.
Knowing how to unlock cells that are unintentionally locked is just as important as knowing how to lock them in the first place. By understanding the potential problems and their solutions, you can efficiently resolve any issues that arise.
Potential Problems and Solutions
Incorrect cell locking can stem from various factors. Understanding the configuration settings is crucial to avoid issues. Misconfigurations or simple errors can lead to unexpected behavior.
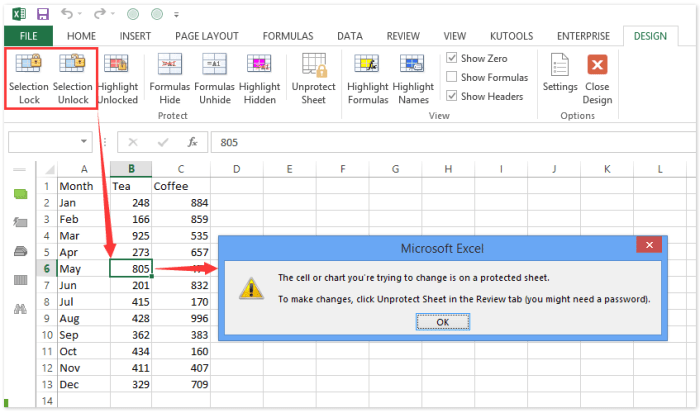
- Locked cells preventing editing: If a cell is locked and you cannot edit it, verify the protection status for the worksheet. Ensure that the worksheet is protected and that the specific cells are locked. If protected, unlock the worksheet or modify the locked cells’ protection attributes. This involves checking the “Protect Sheet” option in the “Review” tab.
- Error messages during locking: Excel may display error messages if the lock attempt violates worksheet protection settings. Common errors include “Cannot lock cells” or “Sheet protection is active.” These errors usually indicate a conflict between your locking action and the protection status of the sheet. Review the sheet protection settings, unlock the sheet if necessary, and then try locking the cells again.
Verify that the sheet is not protected or locked in another application.
- Unintentional locking of necessary cells: Accidental locking of cells used for data entry can hinder workflow. Review the locked cells list and unlock those that are crucial for input. This can be done by using the “Unprotect Sheet” option in the “Review” tab to unlock all cells or selecting individual cells to unlock them. If you accidentally locked cells, use the “Unprotect Sheet” option in the “Review” tab to unlock the worksheet.
Then select the specific cells and uncheck the “Locked” box in the Format Cells dialog box.
Unlocking Locked Cells
Unlocking locked cells is straightforward. Follow these steps to revert a cell to its editable state.
- Unprotect the worksheet: To unlock all cells, unprotect the worksheet using the “Unprotect Sheet” option in the “Review” tab. This will allow all cells to be edited without restrictions. This will also eliminate the need for further cell-specific unlocking.
- Unlock specific cells: If only some locked cells need to be unlocked, select the cells and go to the “Format Cells” dialog box. Locate the “Protection” tab and uncheck the “Locked” option. Click “OK”. This method targets specific cells without affecting other parts of the worksheet.
Error Messages and Explanations
Different error messages can indicate various problems with locking cells. Understanding their meanings is crucial for efficient troubleshooting.
| Error Message | Explanation |
|---|---|
| “Cannot lock cells” | This error suggests that the worksheet is currently protected. Unlock the worksheet to allow locking. |
| “Sheet protection is active” | The sheet protection settings are preventing you from locking cells. Unprotect the sheet to allow locking. |
| “You do not have permission to change the sheet protection.” | Insufficient user privileges. Contact the worksheet administrator or obtain appropriate permissions to modify protection settings. |
Comparison of Locking Methods
Unlocking the power of Excel’s cell protection features involves choosing the right locking method. Different techniques cater to varying needs, offering varying levels of control and flexibility. Understanding the nuances of each approach is crucial for optimizing spreadsheet security and maintainability.Different methods for locking cells in Excel offer varying levels of protection and control. Choosing the right method depends on the specific requirements of your spreadsheet.
This comparison will explore the advantages and disadvantages of each approach, along with situations where one method is superior to another.
Protection Methodologies
Various methods are available for locking cells in Excel, each with its own set of characteristics. The most common methods involve using the worksheet’s protection feature, employing formulas, and implementing custom VBA code. Each method offers distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Worksheet Protection
Worksheet protection is a straightforward method for locking cells. It allows you to protect entire worksheets or specific ranges of cells, preventing accidental changes or modifications.
- Advantages: Simplicity and ease of implementation are key advantages. It’s a quick way to secure a sheet or a range of cells from unintended alterations.
- Disadvantages: Limited granular control over individual cells. You can’t easily restrict access to specific cells within a protected range. Requires the user to manually unprotect the sheet to make changes.
Using Formulas
Using formulas in conjunction with cell locking can provide more specific control over cell contents. Formulas can validate or calculate data within protected cells, limiting input possibilities.
- Advantages: Enhanced data integrity by validating inputs and preventing invalid entries. Formulas can dynamically adjust cell values.
- Disadvantages: Can become complex when implementing advanced validation rules. Requires a basic understanding of formulas.
Custom VBA Code
Custom VBA code offers the most granular control over cell locking. It allows for highly customized and complex scenarios, including complex data validation, advanced restrictions, and even dynamic locking based on specific conditions.
- Advantages: Extremely flexible and allows for intricate control. Can automate locking and unlocking based on user interactions or other events. Offers the most fine-grained control.
- Disadvantages: Requires a good understanding of VBA programming. Implementation can be more time-consuming compared to other methods.
Comparative Table
| Locking Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable Situations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Worksheet Protection | Simple, easy to implement | Limited granular control, requires manual unprotect | Protecting entire sheets or specific ranges from accidental modification |
| Formulas | Data validation, dynamic calculations | Complexity for advanced validation, requires formula knowledge | Restricting inputs to specific values or calculations |
| Custom VBA Code | Highly flexible, granular control, automation | Requires VBA knowledge, time-consuming implementation | Complex scenarios, custom validation, dynamic locking based on conditions |
Illustrative Examples
Unlocking the power of locked cells in Excel isn’t just about preventing accidental changes; it’s about ensuring data integrity and accuracy across various applications. This section provides practical examples of locking different cell types, showcasing their use in financial reports, inventory tracking, and other scenarios. We’ll see how locking cells can significantly improve data reliability and consistency.Understanding how to lock cells is crucial for maintaining the precision and reliability of your Excel spreadsheets.
By restricting edits to specific cells, you safeguard critical data, preventing errors and ensuring the integrity of your analyses.
Financial Reporting
Protecting formulas and constants in financial reports is paramount. Locked cells in this context act as safeguards, preventing unauthorized changes to key figures or calculations. This approach enhances the trustworthiness of your financial analyses.
Example: A spreadsheet for calculating monthly budgets. You want to lock cells containing the initial budget figures entered by management, while allowing for the input of actual spending figures in other cells.
| Cell | Content | Locked? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 2023 Budget (Sales) | Yes | Initial budget value, locked to prevent accidental changes. |
| A2 | 2023 Actual Sales | No | User input for the actual sales figure. |
| B1:B12 | Monthly budget | Yes | Locked, preventing changes to the budget allocations. |
| B13 | Total Budget | Yes | Formula-driven total, locked to maintain accuracy. |
This example demonstrates how locking specific cells ensures that the initial budget figures remain unchanged while allowing adjustments to actual figures. This structure maintains data integrity, and avoids errors that might arise from accidentally altering the budget.
Inventory Tracking
In inventory management, locked cells can protect crucial data points like product codes, unit costs, and reorder levels. This approach ensures accuracy in stock calculations and minimizes errors in inventory reports.
Example: An inventory spreadsheet. You want to lock the product codes and their corresponding unit costs, allowing users to update quantities on hand and calculate values based on these locked parameters.
| Cell | Content | Locked? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1:A10 | Product Codes | Yes | Locked to prevent accidental changes to product identifiers. |
| B1:B10 | Unit Costs | Yes | Locked, ensuring that the cost of each product remains consistent. |
| C1:C10 | Quantity on Hand | No | User input for the current inventory level. |
| D1:D10 | Calculated Value | No | Formula calculating the total value of each product based on quantity and cost. |
By locking the product codes and unit costs, the integrity of the inventory data is maintained. This prevents accidental modification of these essential elements, and ensures that calculations are based on accurate values.
Customization and Design Considerations
Beyond the functionality of locked cells, enhancing their visual presentation significantly improves usability and readability within your Excel spreadsheets. Properly highlighting locked cells can prevent errors and confusion, especially in complex spreadsheets. This section explores various techniques to customize the appearance of locked cells, making them stand out and aid in comprehension.
Customizing Cell Appearance
The basic method of locking cells in Excel often leaves the locked cells indistinguishable from unlocked ones. This section focuses on techniques to make locked cells more prominent.
Highlighting Locked Cells
Different visual cues can effectively highlight locked cells. A simple yet effective approach is to apply a distinctive background color. For instance, a light yellow or a pale blue can clearly mark locked cells without overpowering the overall spreadsheet design. Another option is to use a different font color for the locked cells. A darker color, such as a dark navy blue or dark gray, will stand out against the standard font color.
Visual Cues for Enhanced Readability
To further enhance readability and comprehension, visual cues can be strategically added to locked cells. One method is to use a subtle border around the locked cells. A thin, contrasting border can visually separate locked cells from unlocked cells without being overly distracting. Consider using a different cell fill color, like a very light shade of green or a light orange.
A subtle, yet noticeable, border around the cell can significantly improve the visual separation of locked cells.
Creating a Responsive HTML Table
A responsive HTML table allows for dynamic adjustments based on screen size, ensuring optimal display on various devices. This is crucial for maintaining the visual appeal and readability of locked cells across different viewing environments. Below is an example of how you might implement this:
| Cell Type | Background Color | Border | Font Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| Locked | Light Yellow | 1px solid Dark Gray | Dark Blue |
| Unlocked | White | 1px solid Light Gray | Black |
This example uses a table to visually represent the different styling options for locked and unlocked cells. Adjusting the background colors, border styles, and font colors can be tailored to match the overall design of the spreadsheet. The table demonstrates how the style of locked cells can be easily customized to enhance the clarity of the spreadsheet.
Examples of User-Friendly Forms
Creating user-friendly forms is crucial for efficient data entry and reducing errors. Locking cells strategically in these forms ensures data integrity and prevents accidental modifications, especially important in shared environments or when dealing with sensitive information. These locked cells act as a safeguard, preventing unauthorized changes and maintaining the accuracy of the data.
Data Entry Forms with Locked Cells
Protecting data entry forms is essential. By locking specific cells, you can prevent users from inadvertently altering critical parts of the form. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the collected information. For example, you might lock cells containing calculated values or pre-defined constants, preventing erroneous alterations.
- Customer Order Form: A customer order form can have locked cells for customer ID, order date, and predefined product codes. These fields, often automatically populated or derived from other systems, should remain unchanged to maintain data consistency. Unlocking these fields only for authorized personnel ensures accurate and consistent data.
- Employee Timesheet: In an employee timesheet, the employee ID and project code fields should be locked. These are pre-defined values and shouldn’t be altered by the employee. Only the hours worked and other modifiable fields should be unlocked for input.
Forms with Locked Headers and Calculated Fields
Forms with headers and calculated fields can benefit significantly from locked cells. This ensures that the form’s structure and pre-calculated data remain unchanged. Locking headers prevents accidental deletion or modification, preserving the form’s layout and integrity.
| Item | Quantity | Price | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product A | $10.00 | $10.00 | |
| Product B | $5.00 | $10.00 | |
| Subtotal | $20.00 |
In the example table above, the header row (Item, Quantity, Price, Total) and the calculated “Total” column are locked. Users can only modify the quantity, and the total will automatically update based on the input, maintaining data integrity.
Responsive HTML Table for Forms
Using a responsive HTML table for forms enhances usability across various devices. The locked cells and calculated fields within this table remain consistent, regardless of screen size or device.
| Product | Description | Price | Quantity | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product A | Description for Product A | $10.00 | $10.00 | |
| Product B | Description for Product B | $5.00 | $10.00 | |
| Subtotal | $20.00 |
The responsive HTML table ensures the form’s layout adapts to different screen sizes. The locked header and calculated fields maintain their integrity and position across various devices.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, mastering Lock Cells in Excel empowers you to create robust, secure, and user-friendly spreadsheets. By understanding the different locking methods, you can effectively protect your data from accidental modification, enhance data integrity, and streamline data entry processes. This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed overview of the entire process, from basic techniques to advanced password protection and customization.
Now you’re equipped to confidently use this vital Excel tool.