Do Superscript in PowerPoint sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a step-by-step guide to mastering superscripts in PowerPoint presentations. This guide dives deep into everything from basic insertion methods to advanced formatting techniques, ensuring your presentations are not only informative but also visually appealing and professional. We’ll explore the nuances of superscripts, comparing them to subscripts and demonstrating their practical applications across various presentation elements.
From simple keyboard shortcuts to the power of the Character Map, we’ll uncover the most efficient ways to incorporate superscripts into your work. Learn how to format these crucial elements for maximum readability, considering font sizes, styles, and colors. We’ll also cover advanced techniques, such as custom formatting and precise alignment, allowing you to elevate your presentations to a new level of professionalism.
Introduction to Superscripts in PowerPoint: Do Superscript In PowerPoint
Superscripts, those tiny characters positioned above the baseline of the text, are a valuable tool in presentations for adding precise details and context. They are more than just a formatting choice; they enhance clarity and understanding by providing supplementary information without disrupting the flow of the main text. From scientific formulas to copyright notices, superscripts play a significant role in communicating complex information effectively.Using superscripts in PowerPoint presentations offers a professional and organized way to highlight critical information.
They are particularly useful for denoting exponents, chemical formulas, footnotes, and version numbers, making presentations more informative and comprehensive. Their subtle yet impactful presence elevates the presentation’s overall quality.
Common Uses of Superscripts
Superscripts are frequently employed in presentations to clarify specific information without overwhelming the main text. Their concise nature allows for the inclusion of essential details without disrupting the overall visual hierarchy.
- Exponents: In mathematical expressions, superscripts are fundamental for representing exponents. For example, x 2 denotes x raised to the power of 2.
- Chemical Formulas: In chemistry, superscripts are used to indicate the oxidation state of elements in chemical compounds. For example, Fe 2+ represents an iron ion with a +2 charge.
- Footnotes: Superscripts can be used to denote footnotes, directing the viewer to additional information or sources. This provides context and credibility.
- Version Numbers: Superscripts can be used to highlight the version of a product or software, like software 2.0, signifying an updated version.
- Copyright Information: Superscripts are used to represent copyright notices. For instance, © 2024 indicates the copyright year.
Superscripts vs. Subscripts
Distinguishing between superscripts and subscripts is crucial for accurate representation of information. While both are used for specialized notations, they differ significantly in their meaning and placement.
| Feature | Superscript | Subscript |
|---|---|---|
| Placement | Above the baseline | Below the baseline |
| Meaning | Denotes exponents, footnotes, or other supplementary information. | Indicates the position of an element in a chemical formula or a subscript in a mathematical expression. |
| Example (Mathematical) | x2 | H2O |
| Example (Chemical) | CO2 | Fe2O3 |
| Example (Versioning) | Software3.1 | N/A (Subscripts are not typically used in versioning) |
Superscripts and subscripts play distinct roles in conveying information, each serving a specific purpose in presenting accurate and precise data.
Inserting Superscripts in PowerPoint
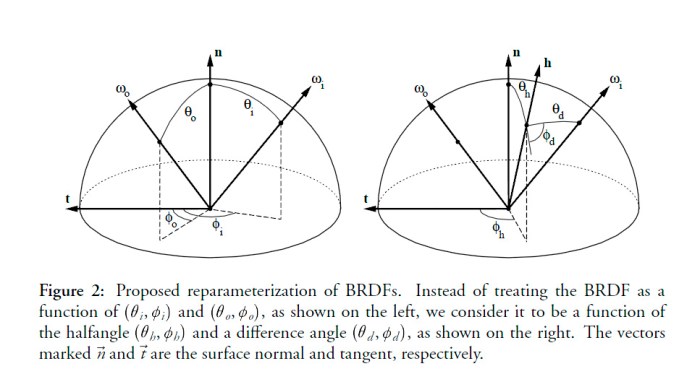
PowerPoint offers several convenient methods for inserting superscripts, which are crucial for mathematical formulas, chemical notations, and various other technical presentations. Understanding these methods can significantly enhance your presentation’s clarity and professionalism. Mastering these techniques will save you time and ensure accuracy in your work.Effectively incorporating superscripts into your PowerPoint slides allows for precise and detailed representation of data, making it easier for your audience to grasp complex information.
Using the correct method will save you time and prevent errors that might hinder your presentation’s effectiveness.
Keyboard Method for Superscripts
This method utilizes the combination of keys for quickly inserting superscripts directly into the text. This approach is straightforward and convenient for simple superscripts.
- Select the text where you want to insert the superscript.
- Press and hold the Ctrl key and the = (equals) key simultaneously.
- Type the characters that should be in the superscript position.
- Release the Ctrl and = keys.
This approach is especially useful for situations requiring quick and repeated insertions of superscripts, ensuring accuracy and maintaining the flow of the document.
Using the Character Map for Superscripts
The Character Map is a valuable tool for inserting a wide range of special characters, including superscripts. This approach allows for the precise selection of a superscript character.
- Open the Character Map application.
- Navigate to the “Symbols” tab.
- Filter by “Subset” for “Superscripts and Subscripts”.
- Select the desired superscript character.
- Click “Select” and then “Copy”.
- Paste the copied character into your PowerPoint slide.
The Character Map is particularly beneficial for inserting non-standard or less frequently used superscripts, ensuring the accuracy of your presentations.
Inserting Superscripts with the Insert Symbol Option
The Insert Symbol option provides a dedicated area for choosing various special characters, including superscripts. This method offers a user-friendly approach to inserting specific superscript symbols.
- Click the “Insert” tab in PowerPoint.
- In the “Symbols” group, click the “Symbol” button.
- Select “More Symbols” from the dropdown menu.
- Choose the “Superscripts and Subscripts” subset.
- Select the desired superscript symbol.
- Click “Insert”.
This approach allows for a comprehensive selection of symbols, ensuring precision and avoiding potential errors in complex presentations.
Comparing Insertion Methods
The keyboard method is the quickest for simple superscripts. The Character Map is best for less common or specialized symbols. The Insert Symbol option provides a wider selection.
Efficiency and Ease Comparison Table
| Method | Efficiency | Ease of Use | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyboard | High | Very High | Fast, simple | Limited character selection |
| Character Map | Medium | Medium | Wide character selection | More steps involved |
| Insert Symbol | Medium | High | Good selection, dedicated area | Slightly more steps than keyboard |
This table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of each method, enabling a comparison of their practical use cases.
Figuring out how to do superscript in PowerPoint can be a bit tricky, but thankfully, there are plenty of online tutorials. Speaking of quirky finds, did you know about this amazing record store in NYC, inside the unlikely new York record store that sells vinyl to the stars ? It’s a great place to get lost in music, just like getting lost in the details of formatting your presentation! Knowing how to do superscript is key for that professional touch in your PowerPoint slides.
Formatting Superscripts in PowerPoint
PowerPoint’s superscript feature allows for concise and professional presentation of information, particularly useful for scientific and technical documents. Mastering superscript formatting ensures your presentations are not only accurate but also visually appealing, making complex data easier to understand at a glance. This section dives into the nuanced aspects of adjusting font size, style, and color, enhancing the overall readability of your superscripts.
Adjusting Font Size and Style
Superscripts, by nature, are smaller than the base text. However, you can tailor their size to complement the overall design of your slide. Adjusting the font size allows for greater clarity and visual hierarchy within your content. Similarly, the font style (e.g., bold, italic) influences how the superscript stands out in the context of the surrounding text.
Choosing the right font style and size significantly impacts readability and professional presentation.
Changing Color and Formatting Characteristics
The color of superscripts can be independently adjusted to distinguish them from the main text or to highlight specific elements. For example, highlighting important variables in a scientific formula with a different color can significantly enhance clarity. In addition to color, other formatting characteristics like underlining or strikethrough can be applied to superscripts, offering more intricate design options to showcase specific elements within your presentation.
This allows for visual differentiation and emphasizes particular details.
Applying Font Styles
Applying font styles such as bold or italic to superscripts provides an additional way to draw attention to specific information. Bolding a superscript can emphasize a crucial element within a formula or equation, while italicizing it might denote a specific variable or unit of measure. Proper use of font styles is essential for conveying the intended meaning of your content effectively.
Different font styles can create visual emphasis, leading to a more visually appealing and understandable presentation.
Importance of Proper Formatting for Readability
Clear and consistent formatting is paramount to ensuring that superscripts are easily readable and understandable. This is especially critical when presenting complex scientific or mathematical concepts. Poor formatting can lead to confusion and errors in interpretation, undermining the clarity of your presentation. Therefore, careful consideration of font size, style, and color is vital for maintaining a high standard of presentation.
Table of Font Styles and Sizes for Superscripts
This table demonstrates various font styles and sizes for superscripts. Note that the optimal size and style will depend on the specific context and design of your presentation.
| Font Style | Font Size (pt) | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Regular | 8 | 2H2O |
| Bold | 9 | 2H2O |
| Italic | 8 | 2H2O |
| Bold Italic | 9 | 2H2O |
| Regular | 10 | 10C2H4 |
Avoiding Common Errors When Using Superscripts
Mastering superscripts in PowerPoint is crucial for clear and professional presentations. However, even seasoned presenters can fall prey to subtle errors that detract from the overall impact of their work. This section focuses on common mistakes and how to avoid them, ensuring your superscripts are accurate and consistent.Many superscript errors stem from the nuances of the formatting process, and the speed at which presentations are often created.
Often, the sheer volume of information and tasks can lead to overlooking details, especially in the rush to complete a presentation. Understanding the root causes of these errors empowers you to proactively prevent them and maintain the precision of your work.
Common Superscript Mistakes
Understanding the common mistakes in superscript usage is crucial for creating presentations that are accurate and professional. By recognizing these pitfalls, you can avoid them and maintain consistency in your work.
- Incorrect Placement: A frequent error involves the placement of the superscript character relative to the text. This can be due to a misunderstanding of the formatting process. The superscript should be directly above and attached to the text it modifies, not floating separately or appearing in an unusual position. Carefully review each instance to ensure alignment and avoid floating superscripts.
- Misaligned Superscripts: Inconsistencies in superscript alignment can create a visually jarring presentation. This happens when superscripts are not aligned properly within a sentence or across multiple lines. A consistent approach to formatting is vital for maintaining visual appeal and clarity. Use the formatting options available in PowerPoint to align superscripts correctly. Employing a consistent style throughout the document ensures readability.
- Typos and Errors in the Text Above the Superscript: Often, the focus is on the superscript itself, but the text preceding it may contain errors. This can be a simple typo or a more complex error. Double-check that the text accompanying the superscript is correct before formatting. Errors in the main text can be as detrimental as errors in the superscript formatting itself.
A thorough proofreading process is essential for ensuring accuracy.
- Missing or Extra Superscripts: This common mistake can happen when adding or removing text or when copying and pasting information from other sources. Ensure the superscript accurately reflects the intended meaning. Carefully examine each piece of text and superscript to avoid missing or adding unnecessary superscripts. This can be particularly problematic when dealing with complex equations or chemical formulas.
Preventing Superscript Errors
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of superscript errors.
Figuring out superscripts in PowerPoint can be a bit tricky, but it’s definitely doable. Speaking of quirky things, have you seen President Obama and Chance the Rapper belt out Jingle Bells? It’s hilarious! watch president obama and chance the rapper sing jingle bells Anyway, once you get the hang of the formatting, adding those tiny numbers above the line in PowerPoint is a breeze.
Just a few clicks and you’re all set!
- Careful Formatting: Double-check the formatting of each superscript after entering it. Pay attention to alignment, placement, and the consistency of your formatting. Use the formatting options within PowerPoint to ensure consistency and avoid inconsistencies that can arise from manually formatting.
- Thorough Proofreading: Always proofread your presentation before delivering it. Focus on the superscripts and the surrounding text. This will help catch errors that might have been missed during the initial creation process. Reviewing the presentation multiple times is often necessary for catching mistakes.
- Templates and Styles: Utilize PowerPoint templates and formatting styles to maintain consistency. Templates provide a structure for formatting elements such as superscripts, ensuring uniformity throughout the presentation. Employing a standardized format can help ensure consistency across your presentation.
- Consistency in Application: A consistent application of superscript formatting is crucial. This ensures readability and prevents visual distractions. Using the same formatting approach consistently is vital for creating a polished and professional presentation.
Troubleshooting Common Superscript Issues
Addressing these issues can save time and improve the presentation’s overall quality.
| Mistake | Solution |
|---|---|
| Incorrect Placement | Carefully review each superscript’s position and adjust as needed. |
| Misaligned Superscripts | Use PowerPoint’s alignment tools to ensure proper alignment. |
| Typos and Errors | Proofread carefully before delivery. |
| Missing or Extra Superscripts | Verify the superscripts match the intended meaning. |
Advanced Techniques for Superscripts
Mastering superscripts in PowerPoint goes beyond the basics. This section delves into advanced formatting techniques, enabling precise control over appearance and integration within your presentations. Custom styles, precise alignment, and controlled spacing are key to achieving professional-looking documents.Customizing Superscript Styles provides a more tailored presentation. Applying these custom formats to superscripts offers flexibility and consistency across your work.
Creating Custom Superscript Styles
Customizing superscript formatting allows for consistent application across multiple slides and documents. This saves time and ensures a uniform appearance. To create a custom superscript style, follow these steps:
- Open the PowerPoint “Styles” pane.
- Select the “New Style” option.
- Choose the “Font” tab and select the desired font, size, and color for the superscript.
- Select the “Effects” tab to adjust the superscript position, and set the “superscript” characteristic.
- Give your new style a descriptive name (e.g., “Citation Font”).
- Apply the style to the desired text.
Applying Custom Formatting to Superscripts
Applying custom formatting to superscripts allows for consistent styling. This ensures a professional and unified look across the entire presentation. The custom style can be applied to any text you want to have superscripted.
- Select the text where you want to apply the custom style.
- In the “Styles” pane, locate and select your newly created custom superscript style.
- The selected text will automatically adopt the formatting characteristics defined in the style.
Precise Alignment of Superscripts
Accurate alignment of superscripts is essential for readability and professional presentation. This involves positioning the superscript relative to the base text.
Figuring out superscripts in PowerPoint can be tricky, but it’s definitely doable! I was recently listening to this beautiful song, Happy Birthday Beautiful Soul , and the uplifting melody reminded me of how important it is to celebrate life’s special moments. Once you master the superscript formatting in PowerPoint, you can make your presentations more visually appealing and professional, so definitely keep practicing!
- Use the “Character Spacing” options within the font formatting to control the horizontal spacing between the base text and the superscript.
- Employ the “Paragraph Spacing” settings to adjust the vertical spacing between the base text and superscript.
- Adjust the superscript position within the “Font” dialog box for fine-tuning.
Controlling Spacing and Positioning
Careful control over the spacing and positioning of superscripts ensures visual clarity and professional presentation.
- Adjust the “Character Spacing” options in the “Font” dialog box to control horizontal spacing. A positive value increases the space between the superscript and base text, while a negative value decreases it.
- Use the “Line Spacing” options in the “Paragraph” dialog box to control the vertical spacing between the superscript and base text. This helps ensure the superscript aligns correctly with the baseline of the main text.
- Employ the “Font” dialog box’s “Effects” options to fine-tune the vertical positioning of the superscript.
Creating and Managing a Superscript Formatting Template, Do Superscript in PowerPoint
Creating a template streamlines the formatting process, saving time and ensuring consistency.
- Create a new slide in PowerPoint.
- Format the superscripts exactly as desired.
- Save the slide as a template for future use.
- Open a new presentation, and choose “Apply Template” to instantly apply the formatted superscript.
Examples of Superscript Usage in Different Presentations
Superscripts, those tiny characters elevated above the baseline, can significantly enhance presentations by adding precision and depth. They’re not just for embellishment; they serve a vital role in clarifying complex information and making presentations more impactful. This section will explore how superscripts are effectively integrated into various presentation types, showcasing examples for different topics and purposes.Using superscripts strategically allows presenters to avoid lengthy explanations or convoluted phrasing, making the information more digestible and memorable for the audience.
Their subtle yet powerful presence clarifies key details and strengthens the overall message of the presentation.
Scientific Presentations
Superscripts are indispensable in scientific presentations. They’re used to represent exponents, chemical formulas, and various notations. For instance, a presentation on chemical reactions could use superscripts to denote the oxidation state of elements, as in the example below:
- In the reaction Fe 2+ + Cu 2+ → Fe 3+ + Cu +, superscripts precisely indicate the changing oxidation states of iron and copper ions.
- A presentation about quantum mechanics might utilize superscripts to express quantum numbers or energy levels, such as n 2.
Mathematical Presentations
Mathematical presentations frequently employ superscripts for exponents and indices. A presentation on calculus might use superscripts to denote derivatives, such as f (n)(x) for the nth derivative of function f.
- Another example involves the binomial theorem, where superscripts are critical for expressing the powers of the variables.
Historical Presentations
In historical presentations, superscripts are useful for citing sources, dates, or specific details. For instance, a presentation on the American Revolution could use superscripts to denote the year a specific event occurred, like the year 1776 th.
- A presentation on the Roman Empire might use superscripts to denote the reign of specific emperors, such as Emperor Claudius th.
- In presentations discussing historical periods, the use of superscripts could be employed to denote the specific years or dates of historical events.
Business Presentations
In business presentations, superscripts can be used to highlight key figures or percentages. For instance, a presentation on market share could use superscripts to denote the percentage increase or decrease.
- A financial presentation might use superscripts to indicate specific financial metrics, such as profit margins (e.g., 10 2%).
Illustrative Example
Imagine a presentation on the growth of a particular company. A slide might include a table showing the revenue figures for the past five years. Using superscripts to indicate the percentage growth from the previous year could make the data more visually appealing and easy to comprehend. The table would clearly show the growth, such as 10% th growth in revenue in year 2023.
This enhances the understanding of the company’s performance and provides a clear visual representation of the growth pattern.
Troubleshooting Superscript Issues
Superscripts, those tiny characters elevated above the baseline, can sometimes cause headaches in PowerPoint presentations. Knowing the common problems and their solutions will save you valuable time and ensure your presentations are polished and professional. This section details potential issues and their remedies, helping you avoid future problems and keep your superscripts looking sharp.
Common Superscript Problems and Their Causes
Superscripts can malfunction due to a variety of reasons. Issues range from simple formatting errors to complex conflicts within the PowerPoint application. Understanding the potential causes is the first step in resolving these problems.
Solutions for Resolving Superscript Issues
Troubleshooting superscript problems in PowerPoint requires a systematic approach. This section presents a structured method for identifying and resolving various issues.
| Problem | Potential Cause | Solution | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superscripts not displaying correctly | Incorrect font selection, formatting issues, or incompatibility between fonts and the PowerPoint version. | Ensure the font used supports superscripts. Check for inconsistencies in formatting, especially if the text is copied from another source. Consider reinstalling or updating the PowerPoint application if issues persist. | 1. Verify the font is compatible with superscripts. 2. Correct any formatting errors, particularly those related to the text style. 3. If problems persist, try a different font or reinstalling PowerPoint. |
| Superscripts disappearing or not showing up | Hidden formatting, conflicting styles, or a PowerPoint bug. | Ensure the superscript formatting is not hidden. Check for any conflicting styles that might override the superscript format. Restart the PowerPoint application. | 1. Check for hidden formatting options or conflicting styles. 2. Verify the formatting is applied correctly. 3. Restart PowerPoint. |
| Superscripts are too small or too large | Incorrect font size, custom formatting, or conflicting settings. | Adjust the font size or the superscript formatting size as needed. Verify that there are no conflicting formatting rules that might override the desired size. | 1. Inspect the font size applied to the text. 2. Adjust the font size of the superscript if needed. 3. Check for conflicting formatting rules. |
| Superscripts are misaligned or overlapping with other text | Incorrect paragraph formatting, improper spacing, or font conflicts. | Adjust the paragraph spacing, or check for conflicts between the font used for the superscript and the main text. Ensure that proper paragraph formatting and spacing is used. | 1. Review the paragraph formatting of the text. 2. Adjust spacing as needed. 3. Confirm there are no font conflicts. |
Preventing Future Superscript Problems
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering superscript issues in your presentations.
- Using Consistent Formatting: Employ consistent formatting throughout your presentation for superscripts. This ensures a uniform appearance and reduces the risk of errors.
- Testing Thoroughly: Test your superscripts across different presentation modes and devices. This can reveal any hidden formatting conflicts or compatibility issues.
- Backing Up Your Work: Regularly back up your PowerPoint presentations. This ensures that you can revert to a previous version if something goes wrong.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, mastering superscripts in PowerPoint is a valuable skill for any presenter. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge and techniques to effectively utilize superscripts across various presentation elements, from titles and headings to bullet points and charts. By understanding the best practices and avoiding common errors, you can ensure that your presentations are not only informative but also visually compelling and professional.
Remember to practice these techniques and refine your presentation skills, and your audience will be sure to appreciate the effort you’ve put into making your content clear and impactful.

Leave a Reply