Get Rid of Bleach Smell is your ultimate guide to conquering that lingering chlorine scent. From identifying the source of the problem to preventing future occurrences, we’ll explore a range of effective solutions. Discover how to banish bleach odors from clothes, carpets, hard surfaces, and the air itself. We’ll even delve into the science behind these stubborn smells, offering you a complete understanding of the issue.
This guide provides detailed methods for removing bleach smells, ranging from simple ventilation techniques to more involved cleaning solutions. We’ll cover everything from using baking soda and vinegar to exploring specialized odor-eliminating products. Plus, we’ll share tips for proper bleach storage and handling to prevent future issues.
Identifying the Source of the Smell

Unpleasant bleach-like odors can be a real nuisance, often stemming from unexpected sources. Pinpointing the culprit is crucial for effective remediation. This involves understanding how bleach interacts with various materials and environments. A thorough investigation into potential culprits can save you time and effort in resolving the issue.Identifying the origin of the bleach smell necessitates a systematic approach. Careful consideration of potential sources and the circumstances surrounding their use is paramount to determining the cause.
This detailed analysis will help you narrow down the possibilities and eliminate those that are unlikely.
Common Household Items That Might Release Bleach-Like Odors
Bleach itself, when used improperly, or in combination with other substances, can produce lingering odors. Understanding the conditions that lead to these odors is crucial to avoiding them in the future. Some materials react with bleach, generating off-gassing that mimics bleach smells.
- Clorox Bleach: The most obvious source. Improper storage, spills, or incomplete rinsing of treated surfaces can result in lingering odors. Improper dilution can also lead to stronger and longer-lasting smells.
- Cleaning products containing bleach: Many cleaning solutions include bleach as an active ingredient. These products can release chlorine-like odors if not used or stored correctly.
- Fabric softener sheets: Although not containing bleach directly, some fabric softener sheets may contain chemicals that react with moisture or other substances, potentially generating a bleach-like smell.
- Certain types of paints or adhesives: Some paints or adhesives contain components that can react with moisture or other substances, potentially producing bleach-like odors, especially during application or drying.
- Disinfectants: Disinfectants, even those not containing bleach directly, can sometimes produce off-gassing that resembles bleach smells.
Ways Bleach Can Be Used and Potential for Lingering Smells
The manner in which bleach is employed significantly impacts the likelihood of lingering smells. Proper techniques are essential to minimize the risk of odor problems.
Getting that lingering bleach smell out of your clothes can be a real pain, but thankfully, there are some great tricks to try. Speaking of creative ways to tackle stubborn smells, did you know that Kelela is collaborating with Skrillex, Clams Casino, and Ratking’s Hak on a new track? It’s a fascinating musical collaboration, and it got me thinking about the surprising connections between art and everyday household tasks.
Regardless of the music, it’s important to find effective ways to get rid of bleach smell for the best results. kelela teams with skrillex clams casino and ratkings hak on new song Hopefully, these ideas help you tackle those tough smells, and you can enjoy fresh clothes without the lingering scent.
- Cleaning: Bleach is a powerful cleaning agent, but improper dilution or application can lead to lingering smells. Incomplete rinsing of treated surfaces can result in a noticeable chlorine-like smell.
- Disinfection: Bleach is commonly used for disinfecting surfaces, and if not adequately rinsed, can leave behind a lingering chlorine scent.
- Laundry: Using bleach in laundry can sometimes produce lingering smells if the laundry isn’t thoroughly rinsed or the bleach concentration is too high.
- Pool maintenance: Using bleach to maintain pools can lead to noticeable odors, particularly if the pool water isn’t adequately balanced or the bleach isn’t diluted correctly.
Distinguishing Between Bleach Smells and Other Similar Scents
Differentiating between bleach odors and other similar scents can be challenging. Careful observation of associated factors is crucial.
| Item | Description | Odor Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Bleach | Household cleaning agent | Strong, sharp, chlorine-like |
| Chlorinated water | Water treated with chlorine | Pungent, often sharp, and similar to bleach |
| Swimming pools | Water treated with chlorine | Strong chlorine smell, often noticeable outdoors |
| Certain cleaning products | Products containing chlorine | May have a sharp, pungent odor similar to bleach |
| Chlorine-based disinfectants | Cleaning solutions containing chlorine | May have a sharp, chlorine-like odor, sometimes more intense than bleach |
Methods for Removing Bleach Smell
Banishing the pungent scent of bleach can be a frustrating task, but with the right approach, you can effectively neutralize the odor and restore a fresh atmosphere. Understanding the underlying causes of the smell, as discussed in the previous sections, is crucial for choosing the most effective removal methods. Different materials and environments will react differently to various cleaning solutions, so a tailored approach is essential.
Ventilation Techniques
Proper ventilation is often the first step in eliminating bleach odors. Fresh air circulation helps to dissipate the chemical compounds that contribute to the lingering smell. Opening windows and doors, using fans, or employing exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms can significantly improve air quality. In enclosed spaces, consider using a dehumidifier to remove moisture, which can sometimes trap the odor.
Prolonged ventilation, especially in conjunction with other methods, often proves highly effective in reducing the bleach smell.
Cleaning Solutions
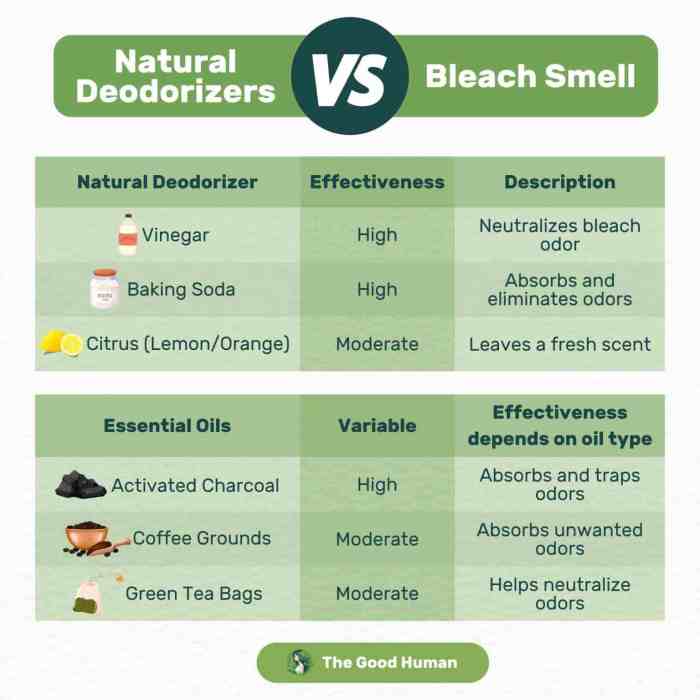
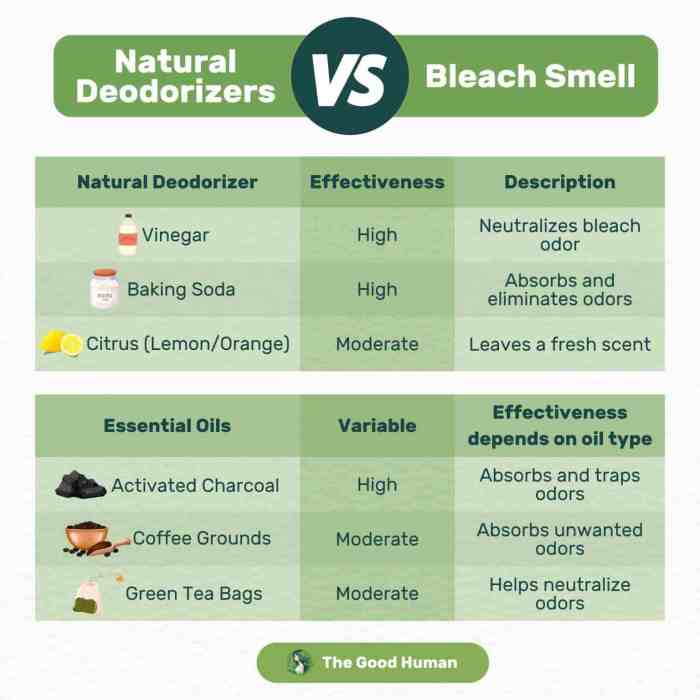
Neutralizing the bleach smell often involves using cleaning solutions that chemically react with the residual bleach. These solutions work by forming less pungent compounds or neutralizing the active ingredients in the bleach. Common cleaning agents, such as vinegar and baking soda, are effective in neutralizing the smell. Choosing the appropriate solution depends on the specific surface and the severity of the odor.
Baking Soda and Vinegar
A popular and effective method for eliminating bleach smells is using a mixture of baking soda and vinegar. Baking soda acts as an absorbent, trapping the lingering bleach molecules. Vinegar, with its acidic properties, helps to break down the bleach residue. The procedure involves mixing baking soda with water to create a paste, applying it to the affected area, allowing it to sit, scrubbing, and then rinsing thoroughly.
This method is particularly useful for porous surfaces like carpets and upholstery.
Comparison of Odor-Eliminating Products
Various commercial odor-eliminating products are available, each claiming to neutralize specific smells. However, the effectiveness of these products can vary. Some products contain enzymes that break down organic matter, while others utilize fragrances to mask the odor. A crucial aspect to consider is the potential for allergic reactions or irritations when using these products, especially for individuals with sensitivities.
Thorough research and careful selection are recommended.
Ugh, bleach smell. It’s a real pain to get rid of, especially if you’re trying to keep your laundry room smelling fresh. Luckily, I just stumbled upon some awesome news about cocorosie announcing a new album plot tour! cocorosie announce new album plot tour Their music always helps me de-stress, and hopefully, a little bit of that positive energy will carry over to conquer that stubborn bleach scent.
Now, back to the task of finding the perfect laundry room air freshener to keep my whites bright and my space smelling great!
Procedure for Using Cleaning Solutions
The following table Artikels the steps for using various cleaning solutions to eliminate bleach smells. These steps are guidelines, and specific adjustments may be necessary based on the surface being treated.
| Method | Materials | Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Using Baking Soda | Baking soda, water | Mix baking soda with water to create a paste. Apply to the affected area, let it sit for approximately 15-30 minutes. Gently scrub the area with a soft brush. Rinse thoroughly with water. |
| Using White Vinegar | White vinegar, spray bottle | Spray the affected area with white vinegar. Allow it to sit for 10-15 minutes. Wipe clean with a damp cloth. |
| Using Commercial Odor Eliminators | Commercial odor eliminator, spray bottle | Follow the manufacturer’s instructions on the product label. Typically, spray the affected area and allow it to sit for the recommended duration. Wipe or blot the area clean as instructed. |
Preventing Bleach Smell in the Future: Get Rid Of Bleach Smell
Keeping your home smelling fresh and avoiding the harsh scent of bleach requires proactive measures. Proper storage, ventilation, and cleaning techniques are crucial to minimizing the risk of lingering bleach odors. By understanding these strategies, you can enjoy a clean home without the unwanted chemical aroma.Effective bleach management involves more than just applying it; it’s about handling it safely and thoughtfully to avoid unwanted odors.
This section focuses on preventative measures to ensure a fresh, clean environment free from the lingering scent of bleach.
Proper Bleach Storage
Proper storage is key to preventing leaks and the release of bleach fumes. Store bleach in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Choose a tightly sealed container to maintain its potency and prevent leakage. Inspect the container regularly for any signs of damage or deterioration. If the container shows any cracks or signs of wear, replace it immediately.
Using a sturdy, leak-proof container is a preventative measure against spills and subsequent odor issues.
Ventilation Best Practices
Adequate ventilation is essential when using bleach. Open windows and doors, and use fans to circulate air, especially in smaller spaces. This helps to dissipate the bleach fumes and prevent them from accumulating. Remember to work in a well-ventilated area to minimize the risk of inhaling bleach vapors. In enclosed spaces, using an exhaust fan or a powerful fan can significantly improve ventilation and help prevent the lingering odor.
Bleach Cleaning Techniques, Get Rid of Bleach Smell
To minimize the possibility of lingering smells, use bleach only as needed and in the correct dilution. Always follow the product instructions carefully, as over-dilution or improper use can contribute to odor problems. Thoroughly rinse surfaces after applying bleach to remove any residue. Allowing surfaces to dry completely is also crucial in preventing lingering smells. For instance, after using bleach to clean a bathroom, open windows to ensure thorough ventilation and allow the area to air out completely.
Preventing Bleach Smells in Specific Areas
- Bathrooms: Maintain good ventilation by opening windows or using exhaust fans. Ensure thorough rinsing after cleaning to remove any bleach residue. Using a bleach-free alternative for occasional cleaning can help prevent buildup of bleach smell.
- Kitchens: Thoroughly clean and rinse surfaces after bleaching. Use a well-ventilated area when cleaning, and use a good exhaust fan if available. Avoid using bleach on food preparation surfaces unless absolutely necessary.
- Laundry Rooms: Open windows or use exhaust fans in the laundry room to remove bleach vapors. Follow the recommended bleach dosage and ensure thorough rinsing of clothes to avoid residue. Consider using a washing machine’s extra rinse cycle to remove bleach residue from clothes.
Step-by-Step Bleach Handling Guide
- Assess the area: Determine if adequate ventilation is available. Open windows and doors, or turn on fans.
- Prepare the solution: Dilute bleach according to product instructions, and always wear appropriate protective gear like gloves and eye protection.
- Apply the solution: Use a sponge or cloth to apply the solution to the affected area, ensuring even coverage. Avoid spraying directly.
- Rinse thoroughly: Rinse the area with clean water to remove any bleach residue.
- Allow to dry: Open windows and allow the area to air dry completely to avoid lingering odors.
- Dispose of used bleach solution responsibly: Never pour bleach down drains, toilets, or sinks. Follow local guidelines for proper disposal.
Addressing Specific Situations
Dealing with bleach smells can be frustrating, but understanding how to target the source and apply the right cleaning methods is key to a fresh-smelling home. Different surfaces react differently to bleach, so a tailored approach is essential for effective removal. This section details specific strategies for eliminating bleach odors from various areas, from clothes to hard surfaces, ensuring a complete solution.
Removing Bleach Odors from Clothes
Bleach stains and odors on clothing often require a multi-step approach. Pre-treating the affected area is crucial. A mixture of oxygen bleach and cool water can often lift the stain and diminish the odor. For tougher stains, consider using a commercial stain remover specifically designed for bleach. Hand-washing or machine-washing, using a gentle cycle and cold water, is generally recommended.
Avoid using hot water, as it can set the stain.
- Pre-treatment: Soak the stained area in a solution of oxygen bleach and cool water for at least 30 minutes before washing.
- Washing: Use a gentle cycle and cold water. Avoid using fabric softeners, as they can trap the bleach odor.
- Drying: Dry the garment in a cool or low heat setting to avoid further setting the odor.
- Additional Steps: If the odor persists, consider using a laundry booster specifically designed for removing odors. Repeated washing with appropriate detergents and pre-treatment methods may be necessary for stubborn stains and odors.
Removing Bleach Odors from Carpets and Upholstery
Bleach odors on carpets and upholstery can be particularly stubborn. A mixture of baking soda and white vinegar is often effective. Baking soda helps to absorb the odor, while vinegar helps neutralize the bleach. Carefully test any cleaning solution on an inconspicuous area first to avoid damage. For heavily soiled areas, professional cleaning services may be necessary.
- Preparation: Blot up any excess moisture with a clean cloth.
- Baking Soda Application: Sprinkle a generous amount of baking soda onto the affected area and let it sit for several hours, or preferably overnight. This will absorb the bleach odor.
- Vinegar Application: Mix equal parts white vinegar and water. Using a clean cloth or sponge, gently apply the solution to the area where baking soda has been sprinkled. Let it sit for a few minutes before blotting up the excess.
- Vacuuming: Vacuum the area thoroughly to remove the baking soda and any remaining moisture.
- Repeat if Needed: If the odor persists, repeat the process.
Eliminating Bleach Odors from Hard Surfaces
Hard surfaces like countertops, sinks, and tiles can also retain bleach odors. A solution of equal parts white vinegar and water can help neutralize the bleach. Always test the solution on an inconspicuous area first. If the odor persists, consider using a commercial cleaner designed for removing bleach stains and odors.
- Cleaning Solution: Mix equal parts white vinegar and water. Apply the solution to the affected area with a clean cloth or sponge.
- Blot Dry: Blot up any excess moisture with a clean cloth.
- Air Dry: Allow the surface to air dry completely.
- Repeat if Needed: If the odor persists, repeat the process.
Removing Bleach Odors from the Air
Bleach odors in the air can be challenging to eliminate. Opening windows and doors to increase ventilation is the first step. Activated charcoal air fresheners can also help absorb the odor. Consider using a dehumidifier, especially in areas with high humidity, as moisture can exacerbate the odor.
Trying to get rid of that lingering bleach smell? It can be a real pain, especially in a laundry room. I was just reading about the sad news of Pan Sonic’s Mika Vainio, who passed away at 53. While that’s a truly heartbreaking story, I’m hoping to find a good natural solution to get rid of bleach smells.
Perhaps baking soda and vinegar could help, or maybe a few drops of essential oil? I’ll be doing some research on different methods to find the best solution for getting rid of the smell. pan sonics mika vainio dead at 53 Hopefully, a fresh, clean scent will be the result!
- Ventilation: Open windows and doors to allow fresh air to circulate.
- Activated Charcoal: Place activated charcoal air fresheners in the affected area.
- Dehumidifier: Consider using a dehumidifier to reduce moisture, as moisture can trap the odor.
- Air Fresheners: Use natural air fresheners like essential oils to mask the smell temporarily.
Strategies for Specific Rooms
Specific rooms, like bathrooms or laundry rooms, may require additional strategies to eliminate bleach odors. In bathrooms, using a combination of ventilation and targeted cleaning solutions can help. In laundry rooms, ensuring proper ventilation and regularly cleaning the area can help minimize the odor.
- Bathrooms: Run the exhaust fan continuously to help clear the air, and use vinegar-based cleaning solutions to neutralize bleach residue.
- Laundry Rooms: Maintain proper ventilation in the laundry room to prevent odor buildup. Clean the washing machine and dryer regularly to remove residue. If the smell comes from the laundry, ensure proper use of laundry detergent and correct bleach use.
Understanding the Science Behind Bleach Odors
Bleach, a powerful cleaning agent, often leaves behind a pungent, chlorine-like odor. This odor isn’t simply an unpleasant byproduct; it stems from specific chemical reactions that occur when bleach interacts with various substances. Understanding these reactions is key to effectively eliminating the smell and preventing its recurrence.
Chemical Reactions Causing Bleach Odors
The characteristic bleach odor arises from the breakdown of hypochlorite ions (OCl⁻) present in bleach solutions. These ions react with organic compounds in the environment, such as those found in fabrics, water, or even the air itself. This reaction often produces volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including chlorinated hydrocarbons, which are responsible for the pungent smell.
HOCl (hypochlorous acid) → OCl⁻ + H⁺
This decomposition can be influenced by various factors, including temperature, moisture, and the presence of other substances.
Impact of Moisture and Temperature
Moisture plays a crucial role in the persistence of bleach odors. Water acts as a solvent, allowing the bleach to interact more readily with other substances, intensifying the reaction and the subsequent odor. Increased temperature accelerates chemical reactions, thus potentially exacerbating the release of volatile compounds responsible for the smell. Higher temperatures also often contribute to more rapid evaporation of these compounds, spreading the odor more quickly.
Different Types of Bleach and Their Impact
Different types of bleach, while all containing hypochlorite ions, may have varying concentrations and formulations. Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) is the most common form. Higher concentrations of sodium hypochlorite can lead to more intense odors due to greater reactivity. Other bleaches, such as calcium hypochlorite, might have different levels of volatility and may release different types of VOCs, resulting in slightly varying odors.
This nuance underscores the importance of tailoring cleaning methods to the specific type of bleach used.
Materials Absorbing or Neutralizing Bleach Odors
Several materials can absorb or neutralize the VOCs released during bleach reactions. Activated charcoal, for example, is known for its excellent adsorption capabilities. Baking soda, with its alkaline properties, can potentially react with some of the acidic components involved in the reaction, reducing the odor. Furthermore, certain materials like natural clays can also help absorb and bind with the volatile compounds.
Chemical Reactions Table
| Substance | Reaction with Bleach | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Water (H₂O) | Dissolves bleach (NaClO), reducing its concentration | Reduces odor intensity as the concentration of the reactive components decreases. |
| Organic Matter (e.g., proteins, fats) | Reacts with hypochlorite ions (OCl⁻), producing chlorinated hydrocarbons | Forms volatile compounds, leading to the characteristic bleach odor. |
| Ammonia (NH₃) | Reacts violently with bleach (OCl⁻), releasing toxic gases | Produces chlorine gas, which is extremely harmful and toxic, and results in a stronger, more unpleasant odor. |
| Baking Soda (NaHCO₃) | Reacts with hypochlorite ions (OCl⁻), potentially neutralizing the odor | Forms sodium chloride (NaCl) and other compounds, potentially reducing the odor. |
| Activated Charcoal | Absorbs volatile compounds | Reduces the concentration of VOCs in the air, effectively masking the smell. |
Last Word
Banishing that persistent bleach smell can be a real challenge, but with the right knowledge and approach, it’s entirely achievable. This guide has equipped you with a wealth of information, from identifying the source of the odor to understanding the science behind it, and offering various methods for effective removal. By following the steps Artikeld, you can confidently tackle bleach smells in any situation and maintain a fresh, clean home.
Remember, proper storage and handling are key to preventing future issues.