What Causes Itchy Legs? This persistent discomfort can be incredibly frustrating, impacting daily life. This comprehensive guide explores the various potential causes, from common skin conditions to underlying medical issues and even lifestyle choices. We’ll delve into the specific symptoms, treatments, and preventative measures to help you understand and manage this irritating problem.
From the dryness of winter air to the irritation of certain fabrics, a multitude of factors can contribute to itchy legs. We’ll investigate the role of allergies, skin conditions, medical problems, and even everyday habits in causing this unwelcome sensation. Understanding these factors is key to finding effective solutions.
Skin Conditions
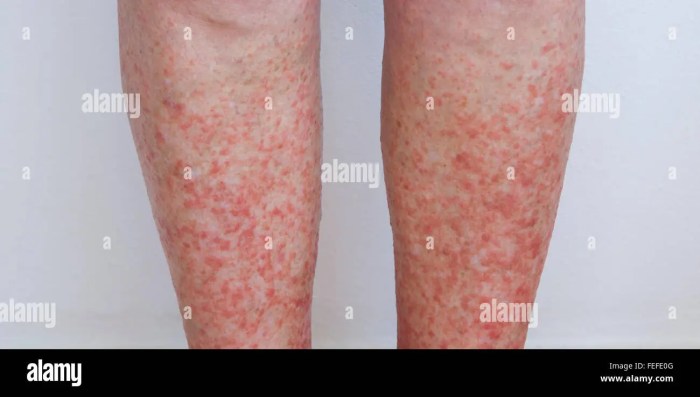
Itchy legs can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience, often stemming from various underlying skin conditions. Understanding these conditions and their symptoms is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. This section delves into common skin ailments that manifest as itchy legs, exploring their characteristics, and providing a comprehensive overview of potential treatments.
Common Skin Conditions Causing Itchy Legs
Several skin conditions can trigger itching in the legs. Identifying the specific condition is essential for targeted treatment.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. On the legs, eczema can manifest as red, scaly patches, often accompanied by small blisters or oozing sores. These areas may be intensely itchy, particularly at night. The itching may be intermittent or persistent.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is another chronic inflammatory skin condition, causing skin cells to build up rapidly. On the legs, psoriasis can present as red, inflamed plaques covered in silvery-white scales. These plaques may be itchy, and the affected areas may feel sore or painful. The itching may worsen during periods of stress or when exposed to triggers.
- Fungal Infections (Tinea): Fungal infections, often referred to as ringworm, can affect various parts of the body, including the legs. These infections manifest as red, scaly patches, often with a ring-like appearance. The skin may be itchy, and the area might be slightly raised or blistered. Fungal infections may be contagious.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions to substances like detergents, cosmetics, or certain foods can lead to itchy legs. The skin reaction may appear as hives, welts, or intensely itchy rashes. These reactions can be localized to the legs or spread across the body, and the itchiness might vary in intensity.
- Contact Dermatitis: Contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin reaction triggered by direct contact with an irritant or allergen. On the legs, this can appear as red, swollen, and itchy skin, often in the area of contact. The reaction may range from mild irritation to severe inflammation, with intense itching being a common symptom.
Symptom Comparison of Skin Conditions
A table outlining the key symptoms of various skin conditions can aid in initial diagnosis.
| Skin Condition | Skin Appearance | Location | Associated Sensations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eczema | Red, dry, scaly, may blister | Flexor surfaces of legs (e.g., behind knees), ankles | Intense itching, burning, stinging |
| Psoriasis | Red, inflamed plaques with silvery-white scales | Any part of the legs, often in patches | Itching, soreness, pain |
| Fungal Infections | Red, scaly, ring-like patches | Any part of the legs | Itching, burning, possible stinging |
| Allergic Reactions | Hives, welts, rash | Various locations on legs, potentially widespread | Intense itching, burning, stinging |
| Contact Dermatitis | Red, swollen, inflamed skin | Area of contact with irritant/allergen | Itching, burning, stinging |
Treatment Options for Skin Conditions
Effective treatment depends on the underlying cause of the itchy legs.
| Condition | Treatment Type | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Eczema | Topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, oral antihistamines | Reduced inflammation, itching relief, improved skin barrier |
| Psoriasis | Topical corticosteroids, topical vitamin D analogs, phototherapy, oral medications | Reduced inflammation, scaling, itching relief, improved skin appearance |
| Fungal Infections | Topical antifungals | Elimination of fungal infection, reduction in itching, scaling |
| Allergic Reactions | Antihistamines, avoidance of allergens | Reduction in allergic response, itching relief |
| Contact Dermatitis | Avoidance of irritant/allergen, topical corticosteroids, calamine lotion | Reduction in inflammation, itching relief, skin healing |
Allergies and Irritants: What Causes Itchy Legs
Itchy legs can often be traced back to allergic reactions or irritants. These triggers can range from common household items to environmental factors, and understanding these culprits is crucial for effective management. Identifying specific triggers allows for targeted avoidance and tailored treatment plans.Allergic reactions and irritations are common causes of itchy legs. These reactions occur when the body’s immune system overreacts to a substance, leading to inflammation and itching.
Irritants, on the other hand, directly damage the skin, causing a similar uncomfortable sensation. Both mechanisms can manifest as itchy legs, underscoring the importance of identifying the specific trigger for effective management.
Common Allergens and Irritants
Numerous substances can trigger allergic reactions or irritate the skin, leading to itchy legs. These include certain fabrics, detergents, and environmental factors. Understanding these potential culprits is key to preventing future episodes.
Types of Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions come in various forms, each with its own mechanisms. Type I hypersensitivity, or immediate hypersensitivity, is characterized by a rapid immune response involving immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. This response often leads to a quick onset of itching and other symptoms. Delayed hypersensitivity reactions, on the other hand, involve a different immune response, with symptoms developing more gradually.
Both types can cause itchy legs, but the timeline of symptoms helps differentiate them.
Summary Table of Allergens and Irritants
| Allergen/Irritant | Symptom Description | Potential Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Certain Fabrics (wool, synthetic fibers) | Skin inflammation, redness, localized itching, often concentrated in areas of contact with the fabric. | Changing to hypoallergenic fabrics, using fabric softeners, avoiding direct contact. |
| Detergents (laundry, dish soap) | Skin irritation, redness, intense itching, particularly around the legs, after contact with contaminated water. | Wearing gloves when handling detergents, rinsing the skin thoroughly after contact, using hypoallergenic detergents. |
| Environmental Allergens (pollen, dust mites) | Generalized itching, sometimes accompanied by rashes, hives, or other skin conditions. Itching can be localized, but it may spread throughout the legs. | Avoiding known allergens, using air purifiers, taking antihistamines. |
| Insect Bites/Stings | Localized itching, redness, swelling, often around the bite site. | Applying cold compresses, using anti-itch creams, seeking medical attention for severe reactions. |
| Certain Cosmetics/Perfumes | Localized itching, redness, skin rash. | Identifying the offending product and avoiding it, using hypoallergenic alternatives, and consulting a dermatologist. |
Importance of Identifying Triggers
Identifying the specific triggers for itchy legs is essential for effective management. Once the causative factors are understood, preventive measures can be implemented. Avoiding known allergens and irritants, using appropriate skin care products, and seeking medical advice when needed will help manage and prevent future episodes of itchy legs.
Medical Conditions
Itchy legs can be a symptom of various underlying medical conditions, extending beyond simple skin irritations. Understanding these conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. These internal health issues can manifest as skin problems, highlighting the intricate connection between internal organs and the skin’s health.Internal health conditions, such as diabetes, thyroid issues, and nerve disorders, can disrupt the body’s natural balance, potentially leading to itching sensations in the legs.
Ever wondered what’s causing those annoying itchy legs? It could be anything from allergies to dry skin, or even a more serious underlying condition. To delve deeper into the complexities of itchy legs, you might find a great resource on how to effectively introduce a journal article in an essay format. Introduce a Journal Article in an Essay provides valuable insight into citing and discussing relevant research, which could potentially reveal more about the causes of itchy legs.
Learning to properly incorporate research helps uncover the reasons behind those pesky leg itches.
These imbalances can affect the skin’s function and sensitivity, contributing to the uncomfortable feeling of itching. The specific mechanisms by which these conditions cause itching can vary, but often involve changes in blood flow, nerve function, or the production of certain hormones or substances.
Medical Conditions Causing Itchy Legs
Various medical conditions can cause itchy legs as a symptom. These conditions often have additional symptoms beyond the itching, making a comprehensive evaluation important.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, potentially leading to diabetic neuropathy. This can cause itching, particularly at night. Peripheral neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, affects the nerves in the extremities, often resulting in tingling, numbness, and itching sensations in the legs. Proper blood glucose control is essential to mitigate the risk of itching and other complications.
- Thyroid Problems: An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) or an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can disrupt hormonal balance, impacting the entire body, including the skin. These imbalances can cause various skin problems, including itching. Hypothyroidism can lead to dry, flaky skin, increasing the susceptibility to itching. Hyperthyroidism can result in increased sweating and warmth, potentially causing skin irritation.
- Nerve Disorders: Conditions like peripheral neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, and other nerve disorders can cause itching in the legs due to damage or dysfunction of the nerves in the extremities. The damaged nerves may send abnormal signals to the brain, interpreting them as itching sensations. Symptoms can vary depending on the specific nerve disorder.
- Kidney Disease: Chronic kidney disease can disrupt the body’s ability to eliminate waste products, potentially leading to the accumulation of toxins. These toxins can affect the skin, leading to itching, which can be particularly intense and widespread. This itching is often associated with other symptoms of kidney disease.
- Liver Disease: Liver problems, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis, can affect the skin’s ability to regulate its moisture balance. This can cause dryness and itching, which is often more noticeable on the legs. The itching may be accompanied by other symptoms associated with liver dysfunction.
Distinguishing Skin-Related vs. Medical Causes
It’s crucial to distinguish between skin-related and medical causes of itchy legs. Skin-related causes typically manifest with localized itching, while medical causes often involve a broader range of symptoms and may affect other parts of the body.
| Condition | Leg-Specific Symptoms | Other Potential Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | Itching, especially at night; tingling, numbness | Increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, slow-healing sores |
| Thyroid Problems | Dry, flaky skin; changes in temperature regulation | Fatigue, weight changes, hair loss, mood swings |
| Nerve Disorders | Itching, burning, tingling, numbness, pain | Muscle weakness, difficulty with coordination, vision problems |
| Kidney Disease | Intense, widespread itching; dry skin | Swelling in the legs and ankles, fatigue, nausea |
| Liver Disease | Dry, itchy skin, especially on the legs | Jaundice, abdominal pain, fatigue, loss of appetite |
Importance of Consulting a Doctor
If you experience persistent itching in your legs, it’s essential to consult a doctor. A medical professional can evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and determine the underlying cause. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively and preventing potential complications. Self-treating can mask the true cause and delay appropriate intervention. A doctor can determine if the itching is a symptom of a broader medical condition requiring specialized care.
Lifestyle Factors
Sometimes, the itchiness in your legs isn’t due to a skin condition or allergy. It can be a result of daily habits and lifestyle choices. Understanding these factors can help you pinpoint the root cause and implement changes for relief. Lifestyle factors significantly influence the health and well-being of the body, including the skin, and can trigger or worsen various skin conditions, including itchy legs.Lifestyle factors play a critical role in the overall health of your skin.
Ever wondered why your legs are itching? It could be anything from dry skin to allergies. Sometimes, though, it’s just a mild annoyance. Interestingly, a recent legal development involving the Walter Becker estate and the dismissal of Donald Fagen’s Steely Dan lawsuit, might not be directly related to itchy legs , but it does highlight the complexities of legal disputes in the music industry.
Regardless, it’s still a good idea to check for common causes like eczema or insect bites if your legs are acting up.
Poor habits can disrupt the body’s natural processes, leading to dry, irritated skin, which often manifests as itchy legs. This section explores how various lifestyle aspects affect your skin and the potential connection to itching.
Stress
Chronic stress can negatively impact the body’s overall functioning. It triggers a cascade of hormonal changes, including elevated cortisol levels. This hormonal surge can disrupt the body’s natural inflammatory response, potentially leading to skin dryness and irritation, which may manifest as itchy legs. For example, individuals experiencing prolonged stress often report increased instances of dry skin, which can exacerbate pre-existing skin conditions.
Lack of Sleep
Adequate sleep is essential for the body’s restorative processes. Sleep deprivation can disrupt hormone balance and impair the body’s ability to repair and regenerate tissues, including the skin. This can lead to skin dryness, increased inflammation, and an increased likelihood of itchy legs. Studies show that individuals who consistently get less than 7-8 hours of sleep are more susceptible to skin issues, including itching.
Poor Diet, What Causes Itchy Legs
A poor diet lacking essential nutrients can negatively impact the skin’s health and overall well-being. A deficiency in vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids can lead to dry, irritated skin, potentially causing itchy legs. For instance, a diet low in omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to dry skin, increasing the likelihood of itching.
Dehydration
Dehydration significantly impacts the skin’s ability to maintain moisture. The skin relies on adequate hydration to retain moisture, forming a protective barrier against external irritants. Insufficient water intake can lead to dry, cracked skin, which is highly susceptible to itching. A well-hydrated body supports healthy skin function, which helps maintain moisture and reduces the chances of itchiness.
Ever wondered what causes those annoying itchy legs? It could be anything from dry skin to allergies, or even a reaction to certain fabrics. Speaking of skin issues and new music, check out Calvin Harris and Ellie Goulding’s new collaboration, “Miracle” here. While you’re enjoying the new tune, remember to keep an eye on any unusual skin changes that might be related to your itchy legs.
Medications
Certain medications can have side effects that include skin irritation and itching. These medications can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier function, leading to dryness and itching. For example, some blood pressure medications and certain antibiotics can cause skin reactions, including itching. Consulting with a doctor is crucial if you suspect a medication is causing itchy legs.
Poor Circulation
Poor circulation can affect the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to the skin. This can result in dry, itchy skin, particularly in the legs. Poor circulation can cause reduced blood flow to the extremities, contributing to dry skin and potentially leading to itchy legs. This is often observed in individuals with conditions affecting blood circulation, such as diabetes or peripheral artery disease.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Pinpointing the cause of itchy legs is crucial for effective treatment. A thorough evaluation, combining medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, is essential to determine the underlying issue. This approach helps tailor the treatment plan to the specific cause, maximizing its effectiveness and minimizing potential side effects.Understanding the diagnostic process and available treatment options empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward managing their itchy legs.
Choosing the right course of action, whether over-the-counter remedies or prescription medications, is essential for symptom relief and overall well-being.
Diagnostic Methods
Accurate diagnosis relies on a combination of methods to identify the root cause of itchy legs. A comprehensive evaluation involves gathering a detailed medical history, physical examination, and relevant tests. These steps help determine the most appropriate treatment strategy.
- Medical History Review: A detailed history of symptoms, including the duration, frequency, and any associated factors like recent changes in environment, medications, or lifestyle, is crucial. This information helps narrow down possible causes and guide the diagnostic process.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination of the skin on the legs, focusing on any visible lesions, rashes, or abnormalities, is essential. The physician assesses the distribution, severity, and characteristics of the itching.
- Skin Biopsies: In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination. This procedure involves removing a small piece of skin tissue, which is then analyzed under a microscope to identify skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or fungal infections. The biopsy procedure typically involves local anesthesia, and the recovery time is usually minimal.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can identify underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the itching. These tests can detect conditions like thyroid problems, anemia, or liver disease. Specific blood tests may include complete blood counts (CBCs), liver function tests (LFTs), and thyroid function tests.
- Allergy Tests: If allergies are suspected, allergy tests can pinpoint specific allergens that may be triggering the itching. These tests can involve skin prick tests, patch tests, or blood tests to identify the specific allergen. Allergy tests help guide treatment strategies, such as avoiding triggers and using antihistamines.
Treatment Approaches
Managing itchy legs involves a range of treatment options, tailored to the specific cause and severity of the condition. A multi-faceted approach, combining lifestyle adjustments, topical medications, and potentially oral medications, often yields the best results.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications: OTC options, such as antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine), hydrocortisone creams, and calamine lotion, are often effective for mild itching. Antihistamines help block the effects of histamine, a chemical released during allergic reactions. Hydrocortisone creams can reduce inflammation and itching, while calamine lotion provides soothing relief. However, OTC options may not be sufficient for severe or chronic cases.
- Prescription Medications: Prescription medications, such as oral antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, or other anti-inflammatory agents, are often prescribed for more severe or persistent itching. These medications can provide stronger symptom relief but may come with potential side effects. The choice of prescription medication depends on the underlying cause and the individual’s response.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing itchy legs. Avoiding known triggers, such as certain fabrics, detergents, or allergens, can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of itching. Maintaining good hydration through drinking plenty of water can also help. Furthermore, applying soothing lotions or moisturizers can provide relief.
Treatment Comparison Table
| Treatment Type | Potential Side Effects | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Over-the-counter antihistamines | Drowsiness, dizziness | Generally effective for mild itching |
| Prescription topical corticosteroids | Skin thinning, skin irritation | Highly effective for reducing inflammation |
| Oral antihistamines | Drowsiness, dry mouth | Effective for allergic reactions |
| Moisturizers | None (generally) | Helps maintain skin hydration, can improve symptoms |
Self-Care Practices
Simple self-care strategies can significantly alleviate itching and promote skin health.
- Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding potential triggers, such as specific fabrics, detergents, or environmental factors, is crucial. This often involves keeping a detailed journal of potential triggers and their association with itching episodes.
- Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration by drinking plenty of water helps keep skin moisturized and prevents dryness, which can exacerbate itching.
- Soothing Lotions and Moisturizers: Applying soothing lotions or moisturizers to the affected area can help alleviate itching and maintain skin hydration. Look for products containing ingredients like aloe vera, oatmeal, or colloidal oatmeal.
Prevention Strategies
Itchy legs can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience. Fortunately, many strategies can help prevent this issue. Proactive measures, including identifying and avoiding triggers, maintaining good skin hygiene, and adopting healthy lifestyle choices, are crucial in managing and preventing itchy legs.Understanding the root causes and triggers of itchy legs is essential for developing a personalized prevention plan. By recognizing what might be contributing to the issue, you can actively work to minimize the risk of experiencing these uncomfortable symptoms.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Identifying potential triggers, such as allergens and irritants, is a key step in preventing itchy legs. Common allergens include certain fabrics, detergents, perfumes, and environmental factors like pollen or dust mites. Irritants, such as harsh soaps or lotions, can also exacerbate the problem. Keeping a detailed log of potential triggers and their corresponding reactions can be helpful in pinpointing the specific substances that trigger itchy legs.
Maintaining Good Skin Hygiene
Proper skin hygiene plays a vital role in preventing itchy legs. Gentle cleansing is key, avoiding harsh soaps or products that can dry out or irritate the skin. Using lukewarm water rather than hot water during showering or bathing can also help. Patting the skin dry instead of rubbing it can further minimize irritation. After cleansing, applying a gentle moisturizer can help maintain skin hydration and prevent dryness.
Diet and Hydration
Diet and hydration significantly influence overall health and skin condition, impacting itchy legs. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially those crucial for skin health, can contribute to preventing dry skin and itchiness. Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids may also support healthy skin. Staying adequately hydrated by drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining skin elasticity and preventing dryness, which can contribute to itchy legs.
Selecting Appropriate Clothing and Bedding
Choosing the right clothing and bedding materials can greatly reduce skin irritation and itching. Opt for breathable fabrics such as cotton, linen, or silk, which allow for better airflow and prevent skin from becoming overly heated or moist. Avoid tight-fitting clothing, which can restrict airflow and cause friction against the skin. Similarly, use hypoallergenic bedding materials to minimize the risk of allergic reactions.
Regularly washing clothing and bedding in mild detergent can also help to remove irritants.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, itchy legs can stem from a variety of sources, ranging from simple skin irritations to more complex medical conditions. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective treatment. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, covering everything from common skin conditions and allergies to lifestyle factors and medical diagnoses. Remember, if the itching persists or worsens, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment.